Java SDK 接入指南
智作工坊 SpeedPix Java SDK,提供简洁易用的 AI 图像生成和处理工作流接口。
资源链接
资源 | 链接 | 描述 |
Maven 包 | 最新版本和历史版本 | |
开源仓库 | 源码、Issue、贡献代码 |
查看 API 文档
授权
获取 API 凭据
创建应用获取
app_key和app_secret
调用 OpenAPI
准备 Java 环境
# 确保 Java 8+
java -version
# 确保 Maven 3.6+
mvn -version配置环境变量
# 设置 API 凭据(推荐方式)
export SPEEDPIX_APP_KEY="your-app-key"
export SPEEDPIX_APP_SECRET="your-app-secret"
export SPEEDPIX_ENDPOINT="https://your-endpoint.com" # 可选安装依赖
Maven:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.speedpix</groupId>
<artifactId>speedpix-java</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<!-- 这里查看新版 https://s01.oss.sonatype.org/#nexus-search;quick~com.aliyun.speedpix -->
</dependency>Gradle:
implementation 'io.github.speedpix:speedpix-java:1.0.0'准备一个已经发布的工作流
在智作工坊控制台中:
参考 工作流管理
创建或选择一个 AI 工作流,可以将以下示例工作流拖入工作流编辑器
这是一个将输入商品图变成白底图的工作流 SDK 测试案例.json,该工作流会自动从用户输入图片抽取商品主体,然后根据用户输入文本生成商品白底图
示范参数:
输入文本
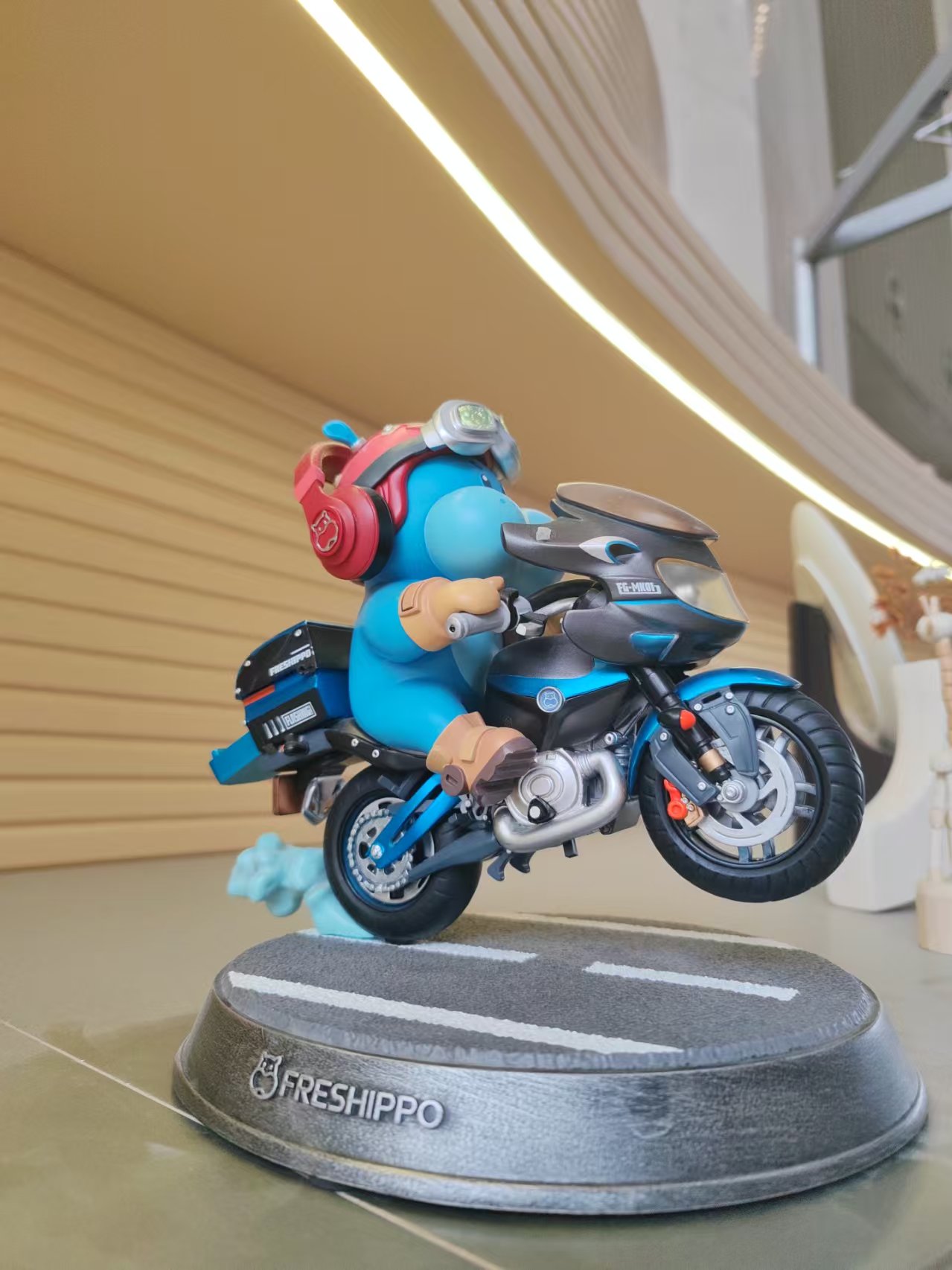
输入图片
输出结果
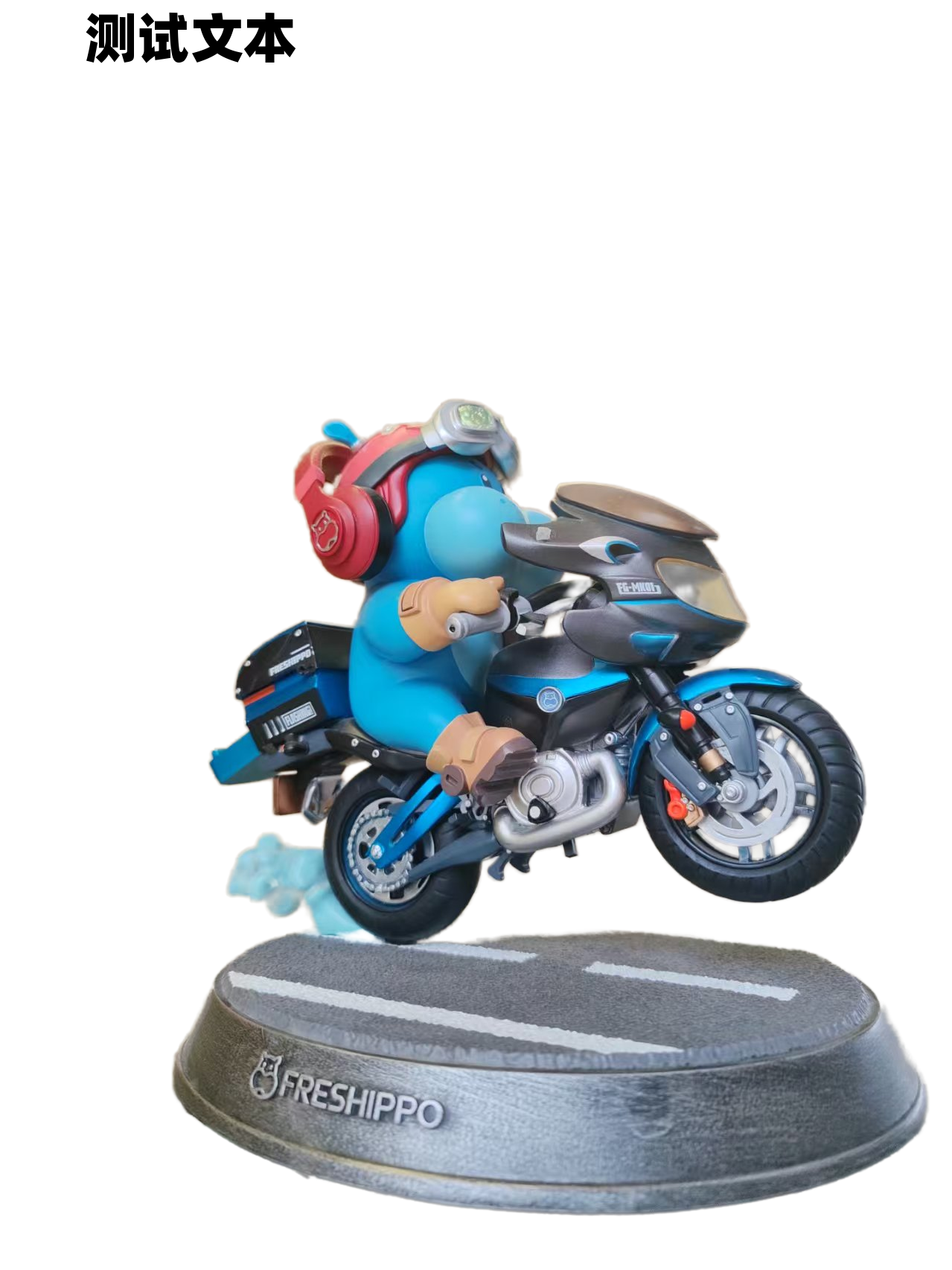
测试文本


发布工作流并获取
workflow_id发布时选择 #1 号节点的 image 字段以及 #6 号节点的 text 作为输入字段
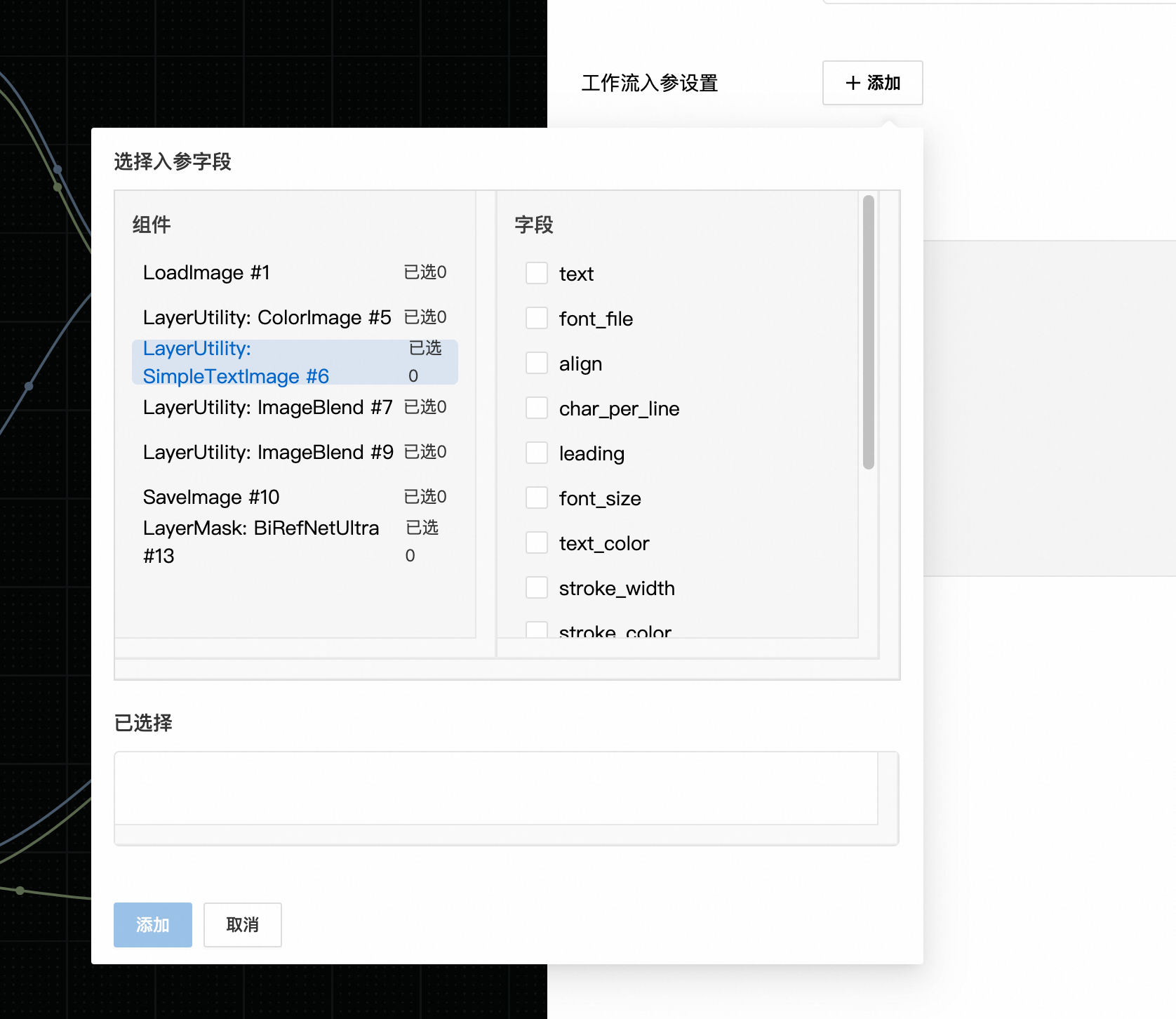
选择 #10 号节点的 images 作为输出字段
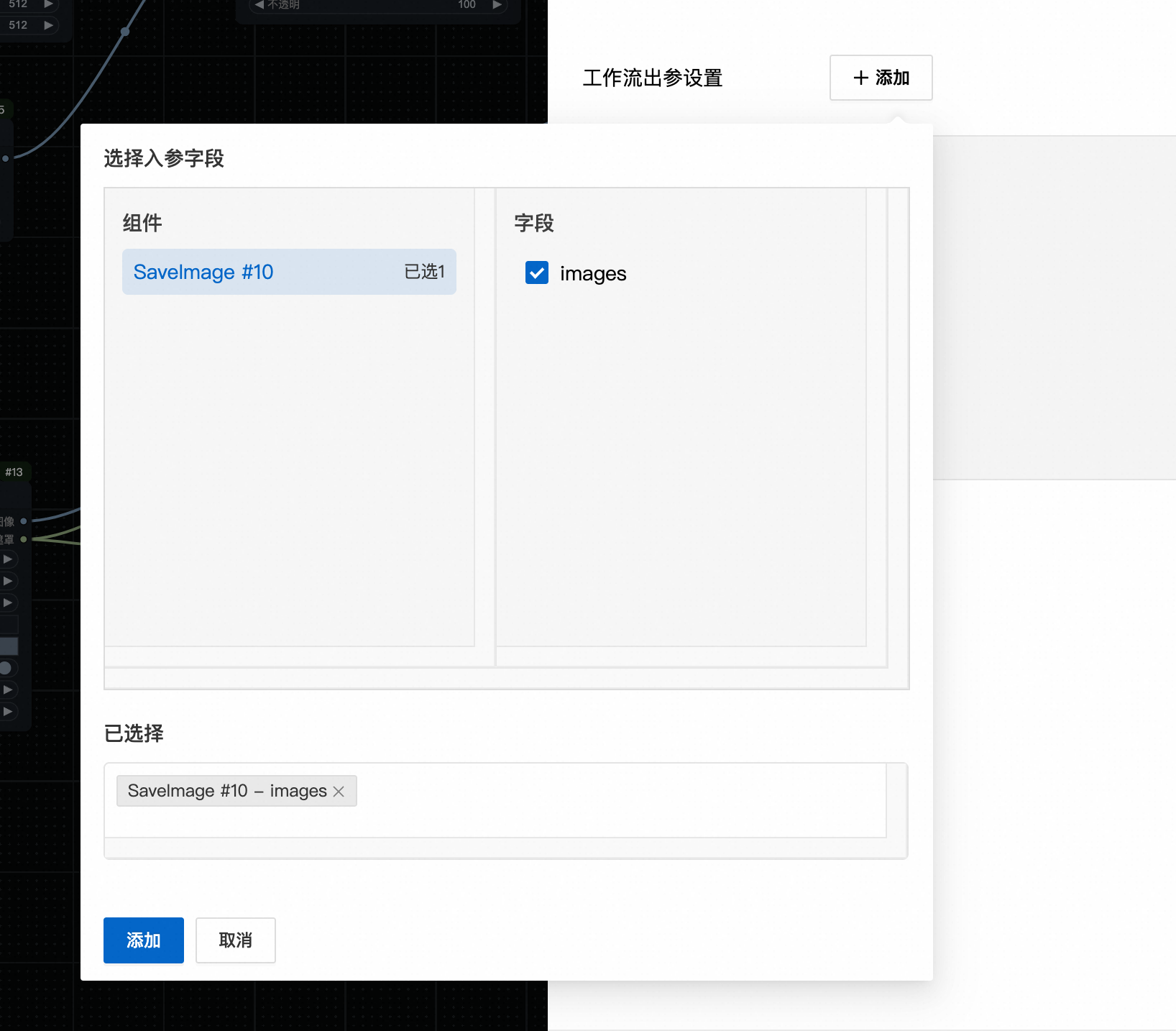
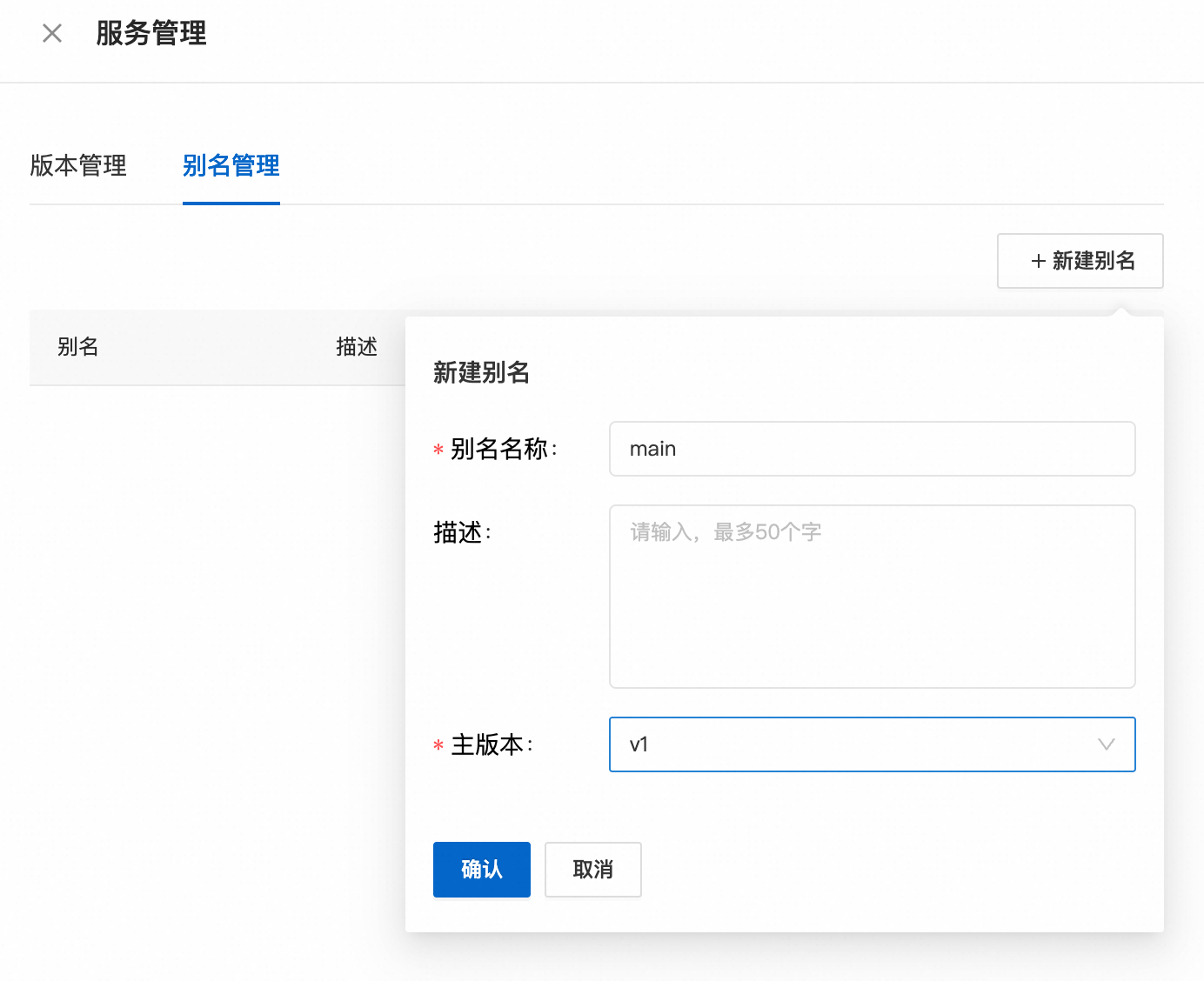
点击提交发布,此时会产生一个 v1 版本,点击右侧别名管理,新建一个 main 别名,映射到 v1 版本,后续我们可以使用该别名调用该工作流,如果需要更新版本,只用在这里切换别名即可,不用代码层变更。
记录工作流的输入、输出格式要求
复制示例代码
方法 1:直接运行(推荐新手)
下载上面案例提到的输入图片到测试工程目录根目录下
package org.example;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPixClient;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ComfyPromptRequest;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.Prediction;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ImageOutput;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class QuickStart {
// 根据工作流输出结构定义结果数据结构
public static class ResultDTO {
private ImageOutput images;
public ImageOutput getImages() {return images;}
public void setImages(ImageOutput images) {this.images = images;}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ResultDTO{images=" + images + '}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建客户端(自动从环境变量读取配置)
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 根据工作流输入准备输入参数
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("text", "盒马");
input.put("image", "./input.jpg"); // 本地文件路径,SDK会自动上传并转换为URL
// 运行 AI 工作流
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your_workflow_id")
.aliasId("main") // 版本别名,默认为 "main"
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 保存结果
if (result.getOutput() != null && result.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
result.getOutput().getImages().save("result.png");
System.out.println("图片已保存为 result.png");
}
}
}方法 2:全局函数
package org.example;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPix;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ComfyPromptRequest;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ImageOutput;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.Prediction;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class GlobalFunctionExample {
// 定义结果数据结构
public static class ResultDTO {
private ImageOutput images;
public ImageOutput getImages() {return images;}
public void setImages(ImageOutput images) {this.images = images;}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ResultDTO{images=" + images + '}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 准备输入参数
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("text", "盒马");
input.put("image", "./input.jpg"); // 本地文件路径,SDK会自动上传并转换为URL
// 使用全局函数运行
Prediction<ResultDTO> output = SpeedPix.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your_workflow_id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
if (output.getOutput() != null && output.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
output.getOutput().getImages().save("result.png");
System.out.println("图片已保存为 result.png");
}
}
}方法 3:传统预测接口(完全控制)
package org.example;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPixClient;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ComfyPromptRequest;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ImageOutput;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.Prediction;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.exception.PredictionException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TraditionalExample {
// 定义结果数据结构
public static class ResultDTO {
private ImageOutput images;
public ImageOutput getImages() {return images;}
public void setImages(ImageOutput images) {this.images = images;}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ResultDTO{images=" + images + '}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 准备输入参数
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("text", "盒马");
input.put("image", "./input.jpg"); // 本地文件路径,SDK会自动上传并转换为URL
try {
// 创建预测任务
Prediction<ResultDTO> prediction = client.predictions().create(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your_workflow_id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
System.out.println("创建预测任务: " + prediction.getId());
// 等待完成
prediction = prediction.waitForCompletion();
if (prediction.getOutput() != null && prediction.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
prediction.getOutput().getImages().save("result.png");
}
} catch (PredictionException e) {
System.err.println("预测失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}执行测试
# 编译并运行测试脚本
mvn compile exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="QuickStart"
# 验证安装
mvn dependency:tree | grep speedpix
# 检查生成的文件
ls -la result.png资源配置
共享算力 vs 独享资源
智作工坊支持两种资源类型:
共享算力:默认使用,成本较低,适合一般业务场景
独享资源:推荐对延迟和成功率敏感的业务使用,提供更稳定的性能保障
配置方式
默认情况下,如果不指定资源配置,系统会使用共享算力资源。如果您对延迟和成功率有较高要求,推荐配置独享资源。
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPixClient;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ComfyPromptRequest;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.Prediction;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
// 使用共享算力(默认)
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("prompt", "一个美丽的风景");
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 不指定 resourceConfigId 时自动使用共享算力
// 使用独享资源
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.resourceConfigId("your-dedicated-resource-id") // 指定独享资源ID
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 使用静态方法指定独享资源
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = SpeedPix.run(
ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.inputs(input)
.build(),
"your-dedicated-resource-id", // 独享资源ID参数
ResultDTO.class
);相关文档
SDK API 完整参数说明
1. 构造函数 - new SpeedPixClient(...)
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient(endpoint, appKey, appSecret, userAgent, timeoutSeconds);参数说明:
参数 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
endpoint | String | https://openai.edu-aliyun.com | API 端点地址 |
appKey | String | 环境变量 SPEEDPIX_APP_KEY | 应用密钥 |
appSecret | String | 环境变量 SPEEDPIX_APP_SECRET | 应用密码 |
userAgent | String | speedpix-java/1.0.0 | 用户代理字符串 |
timeoutSeconds | int | 30 | 请求超时时间(秒) |
示例:
// 使用环境变量(推荐)
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 完整配置
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient(
"https://your-endpoint.com",
"your-app-key",
"your-app-secret",
"my-app/1.0.0",
60
);
// Builder 模式
SpeedPixClient client = SpeedPixClient.builder()
.appKey("your-app-key")
.appSecret("your-app-secret")
.endpoint("https://custom-endpoint.com")
.userAgent("my-app/1.0.0")
.timeoutSeconds(60)
.build();2. 运行工作流 - client.run()
Prediction<T> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest request, Class<T> outputType);参数说明:
参数 | 类型 | 必需 | 默认值 | 说明 |
workflowId | String | 是 | - | 工作流 ID |
inputs | Map<String, Object> | 是 | - | 工作流输入参数 |
aliasId | String | 否 | "main" | 版本别名 |
versionId | String | 否 | - | 版本 ID(与 aliasId 二选一) |
randomiseSeeds | Boolean | 否 | false | 是否随机化种子 |
returnTempFiles | Boolean | 否 | false | 是否返回临时文件 |
文件路径自动处理:
SDK 会自动识别 input 中的文件路径参数
支持相对路径(如
./image.jpg)和绝对路径自动上传文件并替换为可访问的 URL
支持常见格式:jpg, png, gif, bmp, webp, mp4 等
示例:
// 基础用法
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("prompt", "生成图片");
input.put("image", "./source.jpg"); // 自动上传
input.put("strength", 0.8);
input.put("steps", 20);
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("workflow-123")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 高级用法
Map<String, Object> advancedInput = new HashMap<>();
advancedInput.put("prompt", "风格转换");
advancedInput.put("source_image", "./input.jpg");
advancedInput.put("style_image", "/Users/you/style.png");
advancedInput.put("control_image", "./control.jpg");
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("workflow-123")
.aliasId("v2.1")
.inputs(advancedInput)
.randomiseSeeds(true)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);3. 预测管理 - client.predictions
3.1 创建预测 - predictions.create()
Prediction<T> prediction = client.predictions().create(ComfyPromptRequest request, Class<T> outputType);参数说明:
参数 | 类型 | 必需 | 说明 |
workflowId | String | 是 | 工作流 ID |
inputs | Map<String, Object> | 是 | 输入参数 |
aliasId | String | 否 | 版本别名 |
versionId | String | 否 | 版本 ID |
randomiseSeeds | Boolean | 否 | 是否随机化种子 |
returnTempFiles | Boolean | 否 | 是否返回临时文件 |
3.2 获取预测 - predictions.get()
Prediction<T> prediction = client.predictions().get(String predictionId, Class<T> outputType);示例:
// 创建预测
Prediction<ResultDTO> prediction = client.predictions().create(
ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("workflow-123")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(),
ResultDTO.class
);
// 获取预测状态
Prediction<ResultDTO> updated = client.predictions().get(prediction.getId(), ResultDTO.class);
// 等待完成
prediction = prediction.waitForCompletion();4. 文件管理 - client.files
4.1 上传文件 - files.create()
FileObject file = client.files().create(File file);
FileObject file = client.files().create(Path path);
FileObject file = client.files().create(InputStream inputStream, String filename);参数说明:
参数 | 类型 | 必需 | 说明 |
file | File | 是 | 文件对象 |
path | Path | 是 | 文件路径 |
inputStream | InputStream | 是 | 输入流 |
filename | String | 否 | 自定义文件名 |
示例:
// 上传本地文件
File imageFile = new File("./image.jpg");
FileObject file1 = client.files().create(imageFile);
// 上传路径
Path imagePath = Paths.get("./image.png");
FileObject file2 = client.files().create(imagePath);
// 上传流
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./image.gif")) {
FileObject file3 = client.files().create(fis, "image.gif");
}
// 在工作流中使用上传的文件
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("image", file1.getUrl()); // 使用文件URL
input.put("prompt", "处理图片");
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("workflow-123")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);5. 预测对象方法
5.1 等待完成 - prediction.waitForCompletion()
Prediction<T> result = prediction.waitForCompletion();示例:
// 创建预测但不等待
Prediction<ResultDTO> prediction = client.predictions().create(request, ResultDTO.class);
// 手动等待完成
Prediction<ResultDTO> completed = prediction.waitForCompletion();
// 检查状态
if ("succeeded".equals(completed.getStatus())) {
completed.getOutput().getImages().save("result.png");
}6. 图像输出对象 - ImageOutput
当工作流返回图像时,可以使用 ImageOutput 对象进行处理:
ImageOutput images = result.getOutput().getImages();
// 保存到本地文件
images.save("result.png");
// 获取输入流
InputStream stream = images.getInputStream();
// 获取原始数据
byte[ ] data = images.getData();
7. 全局函数
7.1 模块级运行 - SpeedPix.run()
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPix;
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = SpeedPix.run(ComfyPromptRequest request, Class<ResultDTO> outputType);使用默认客户端(从环境变量配置)。
8. 错误处理
import com.aliyun.speedpix.exception.PredictionException;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.exception.SpeedPixException;
try {
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(request, ResultDTO.class);
result.getOutput().getImages().save("result.png");
} catch (PredictionException e) {
System.err.println("预测错误: " + e.getMessage());
System.err.println("预测ID: " + e.getPrediction().getId());
System.err.println("错误详情: " + e.getPrediction().getError());
} catch (SpeedPixException e) {
System.err.println("API错误: " + e.getMessage());
if (e.getErrorCode() != null) {
System.err.println("错误码: " + e.getErrorCode());
}
if (e.getApiInvokeId() != null) {
System.err.println("调用ID: " + e.getApiInvokeId());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("操作被中断: " + e.getMessage());
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("文件操作失败: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("未知错误: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}更多使用方式
// 方式1:最简单(推荐新手)
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPix;
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("prompt", "test");
input.put("image", "./input.jpg"); // 文件路径会自动上传并转换
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = SpeedPix.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("workflow-id")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 方式2:实例化客户端
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("workflow-id")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 方式3:完全控制(高级用户)
Prediction<ResultDTO> prediction = client.predictions().create(request, ResultDTO.class);
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = prediction.waitForCompletion();文件上传示例
上传本地文件
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPixClient;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.FileObject;
public class FileUploadExample {
public static void main(String[ ] args) throws Exception {
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 1. 上传本地文件
FileObject file = client.files().create(new File("./input-image.jpg"));
// 2. 在工作流中使用文件URL
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("image", file.getUrl()); // 使用上传后的文件URL
input.put("prompt", "处理这张图片");
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 3. 保存结果
if (result.getOutput() != null && result.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
result.getOutput().getImages().save("processed-result.png");
System.out.println("处理后的图片已保存");
}
}
}多文件上传
public class MultiFileExample {
public static void main(String[ ] args) throws Exception {
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 上传多个文件
FileObject backgroundImage = client.files().create(new File("./background.jpg"));
FileObject maskImage = client.files().create(new File("./mask.png"));
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("background_image", backgroundImage.getUrl());
input.put("mask_image", maskImage.getUrl());
input.put("prompt", "替换背景");
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
if (result.getOutput() != null && result.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
result.getOutput().getImages().save("composite-result.png");
}
}
}常见文件参数示例
// 根据工作流的输入要求,文件参数可能是:
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
// 图片类型
input.put("image", fileUrl);
input.put("input_image", fileUrl);
input.put("background_image", fileUrl);
// 路径类型
input.put("image_path", fileUrl);
input.put("file_path", fileUrl);
// 文件类型
input.put("file", fileUrl);
input.put("input_file", fileUrl);
// 配合文本提示
input.put("prompt", "your text prompt");
input.put("negative_prompt", "unwanted elements");完整示例:图像处理流程
端到端图像处理示例
import com.aliyun.speedpix.SpeedPixClient;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ComfyPromptRequest;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.Prediction;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.FileObject;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.model.ImageOutput;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.exception.PredictionException;
import com.aliyun.speedpix.exception.SpeedPixException;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CompleteExample {
public static class ResultDTO {
private ImageOutput images;
private ImageOutput preview;
public ImageOutput getImages() { return images; }
public void setImages(ImageOutput images) { this.images = images; }
public ImageOutput getPreview() { return preview; }
public void setPreview(ImageOutput preview) { this.preview = preview; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ResultDTO{images=" + images + '}';
}
}
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
try {
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 检查输入文件是否存在
File inputFile = new File("./input.jpg");
if (!inputFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("请准备一个名为 input.jpg 的图片文件");
return;
}
System.out.println("正在上传文件...");
FileObject uploadedFile = client.files().create(inputFile);
System.out.println("文件上传成功: " + uploadedFile.getId());
System.out.println("正在处理图像...");
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("image", uploadedFile.getUrl());
input.put("prompt", "enhance the image quality, make it more vivid");
input.put("strength", 0.8);
input.put("guidance_scale", 7.5);
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.aliasId("main")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
System.out.println("处理完成!");
// 保存所有输出
if (result.getOutput() != null) {
if (result.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
result.getOutput().getImages().save("enhanced-output.png");
System.out.println("增强后的图片已保存为: enhanced-output.png");
}
// 如果有多个输出
if (result.getOutput().getPreview() != null) {
result.getOutput().getPreview().save("preview.png");
System.out.println("预览图已保存为: preview.png");
}
}
} catch (PredictionException e) {
System.err.println("预测失败: " + e.getMessage());
if (e.getPrediction() != null) {
System.err.println("预测ID: " + e.getPrediction().getId());
System.err.println("错误详情: " + e.getPrediction().getError());
}
} catch (SpeedPixException e) {
System.err.println("API 错误: " + e.getMessage());
System.err.println("请检查参数配置");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.err.println("处理被中断,请稍后重试");
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("未知错误: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}批量处理示例
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class BatchProcessingExample {
public static void main(String[ ] args) throws Exception {
SpeedPixClient client = new SpeedPixClient();
// 批量处理多个文件
List<String> inputFiles = Arrays.asList(
"./input1.jpg",
"./input2.jpg",
"./input3.jpg"
);
for (int i = 0; i < inputFiles.size(); i++) {
String inputPath = inputFiles.get(i);
System.out.println("处理文件 " + (i + 1) + "/" + inputFiles.size() + ": " + inputPath);
try {
// 上传文件
FileObject uploadedFile = client.files().create(new File(inputPath));
// 处理图像
Map<String, Object> input = new HashMap<>();
input.put("image", uploadedFile.getUrl());
input.put("prompt", "enhance and stylize this image");
Prediction<ResultDTO> result = client.run(ComfyPromptRequest.builder()
.workflowId("your-workflow-id")
.inputs(input)
.build(), ResultDTO.class);
// 保存结果
if (result.getOutput() != null && result.getOutput().getImages() != null) {
String outputPath = "output_" + (i + 1) + ".png";
result.getOutput().getImages().save(outputPath);
System.out.println("已保存: " + outputPath);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("处理失败 " + inputPath + ": " + e.getMessage());
}
}
System.out.println("批量处理完成!");
}
}