漏斗分析是常见的转化分析方法,可以分析用户在各个阶段的行为转化率,帮助管理者或运营等角色通过转化率来衡量每个阶段的转化情况,从而达到优化产品,提升转化率的目的,被广泛应用于用户行为分析和App数据分析的流量分析、产品目标转化等数据运营与数据分析领域。
背景信息
事件(Event)代表了用户的某个或一系列有意义的行为,比如游戏App的下载、注册、登录等,通过分析用户的各项行为数据还原用户真实的使用过程,从而提升产品转化率,助力业务增长。常见的用户行为分析包括事件分析、漏斗分析、留存分析等。漏斗函数主要用于分析一个多步骤过程中每一步的转化与流失情况,通过分析漏斗模型中每一步的指标,对业务的转化一目了然。例如一个游戏客户的完整流程可能包含以下步骤:登录账号>进入游戏>游戏操作>关卡结算>账号退出等,可以通过漏斗函数将这些特定目标过程中的行为设置为一个漏斗,分析每一步的转化情况,以帮助业务实现精细化数据分析,优化产品体验,提升转换率等。
基本概念
关于漏斗分析的基本概念如下:
事件:需要分析的相关操作。
转化步骤:由多个事件组成的分析流程,严格按照每一步进行漏斗计算。
时间范围:事件发生的时间范围,是指漏斗的第一个步骤发生的时间范围。
窗口期:完成漏斗的时间限制,即仅在该时间范围内,从第一个步骤进行到最后一个步骤,才能被视为一次成功的转化。
相关概念对应到具体分析界面如下图:
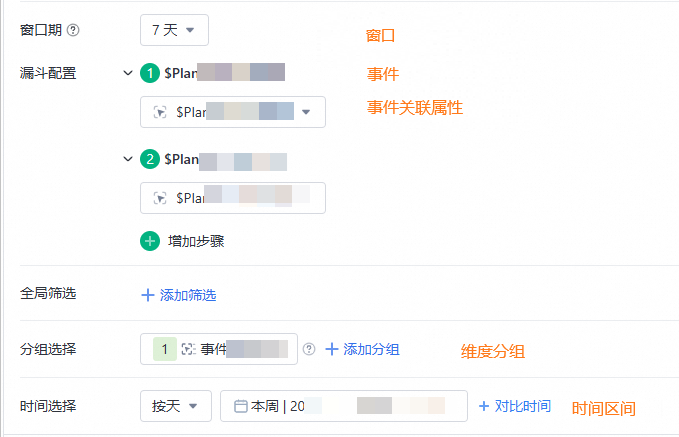
漏斗函数介绍
Hologres是阿里云自研的一站式实时数仓,支持多种场景的实时数据多维分析。在用户行为分析场景上,Hologres提供多种漏斗函数,快速高效地帮助业务进行用户行为分析,被广泛应用在互联网、电商、游戏等行业客户的用户分析场景中。
当前Hologres支持的漏斗函数包括:基础漏斗函数(windowFunnel)、区间漏斗函数(range_funnel)、属性关联漏斗函数(finder_funnel)和维度分组漏斗函数(finder_group_funnel)。
各函数描述及功能支持情况如下:
漏斗函数 | 函数描述 | 功能支持情况 | ||||
设置窗口期(window) | 设置漏斗事件(event) | 事件属性关联(attr_realted) | 维度分组(group_event_index) | 时间范围(start_timestamp) | ||
支持在特定的窗口期内计算事件的漏斗结果。 | 支持 说明 仅允许设置一个较短的时间窗口(比如几小时、一天之内),不支持将多个自然日作为窗口。 | 支持 | 不支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | |
支持在特定的窗口期内计算事件的漏斗结果,且支持按照时间字段对结果进行分组展示。 | 支持 说明 支持将多个自然日作为窗口。 | 支持 | 不支持 | 支持 说明 仅支持按照时间分组。 | 支持 | |
支持在特定的窗口期内计算事件的漏斗结果,且可以指定事件关联属性,但不能按照时间进行分组。 | 支持 说明 支持将多个自然日作为窗口。 | 支持 | 支持 | 不支持 | 支持 | |
支持在特定的窗口期内计算事件的漏斗结果,且可以按照任意字段对结果进行分组展示,并指定事件的关联属性。 | 支持 说明 支持将多个自然日作为窗口。 | 支持 | 支持 | 支持 说明 支持按照任意字段分组。 | 支持 | |
属性关联:是指任意事件可以按照属性进行关联。例如游戏场景中,设置的漏斗为登录账号>进入游戏>游戏操作>关卡结算>账号退出等,并为每个事件设置了“国家”的属性,此时就可以将该属性作为关联ID,保证每个步骤转化都是按照同一个属性值作为转化。漏斗函数不同步骤关联的属性可以是相同属性,也可以是不同属性,但是要求属性的类型必须一致。
维度分组:是指按照不同的维度对结果进行分组展示。例如按天分组,按国家、IP分组等,以实现更细粒度的漏斗分析,一个用户只能出现在一个分组中,如果不属于某个分组,将会被归类到“unreach”组。
