本文为您介绍如何创建和操作DataFrame对象,以及使用DataFrame完成基本的数据处理。
数据准备
本文将以u.user、u.item和u.data数据进行举例。其中u.user是用户相关的数据,u.item是电影相关的数据,u.data是评分相关的数据。
创建表:
pyodps_ml_100k_users(用户相关的数据)。CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS pyodps_ml_100k_users ( user_id BIGINT COMMENT '用户id', age BIGINT COMMENT '年龄', sex STRING COMMENT '性别', occupation STRING COMMENT '职业', zip_code STRING COMMENT '邮编' );pyodps_ml_100k_movies(电影相关的数据)。CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS pyodps_ml_100k_movies ( movie_id BIGINT COMMENT '电影 ID', title STRING COMMENT '电影标题', release_date STRING COMMENT '上映日期', video_release_date STRING COMMENT '视频发布日期', IMDb_URL STRING COMMENT 'IMDb 链接', unknown TINYINT COMMENT '未知', Action TINYINT COMMENT '动作', Adventure TINYINT COMMENT '冒险', Animation TINYINT COMMENT '动画', Children TINYINT COMMENT '儿童', Comedy TINYINT COMMENT '喜剧', Crime TINYINT COMMENT '犯罪', Documentary TINYINT COMMENT '纪录片', Drama TINYINT COMMENT '戏剧', Fantasy TINYINT COMMENT '奇幻', FilmNoir TINYINT COMMENT '黑色电影', Horror TINYINT COMMENT '恐怖', Musical TINYINT COMMENT '音乐', Mystery TINYINT COMMENT '悬疑', Romance TINYINT COMMENT '浪漫', SciFi TINYINT COMMENT '科幻', Thriller TINYINT COMMENT '惊悚', War TINYINT COMMENT '战争', Western TINYINT COMMENT '西部' );pyodps_ml_100k_ratings(评分相关的数据)。CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS pyodps_ml_100k_ratings ( user_id BIGINT COMMENT '用户id', movie_id BIGINT COMMENT '电影id', rating BIGINT COMMENT '得分', timestamp BIGINT COMMENT '时间戳' )
基于Tunnel Upload 将本地数据文件内容导入MaxCompute的表中。更多Tunnel操作,请参见Tunnel命令。
Tunnel upload -fd | path_to_file/u.user pyodps_ml_100k_users; Tunnel upload -fd | path_to_file/u.item pyodps_ml_100k_movies; Tunnel upload -fd | path_to_file/u.data pyodps_ml_100k_ratings;
DataFrame对象操作
现在已经有了三张表,分别是pyodps_ml_100k_movies(电影相关的数据)、pyodps_ml_100k_users(用户相关的数据)、pyodps_ml_100k_ratings(评分相关的数据)。以下示例使用IPython运行。
确保已经安装了Python。IPython是基于Python的,所以需要先安装Python环境。接着通过pip install IPython 安装IPython。安装完成后,可以通过执行IPython命令来启动IPython的交互式环境,开始编写和执行Python代码。
创建ODPS对象。
import os from odps import ODPS # 确保 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID 环境变量设置为用户 Access Key ID, # ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET 环境变量设置为用户 Access Key Secret, # 不建议直接使用 Access Key ID / Access Key Secret 字符串 o = ODPS( os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID'), os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'), project='your-default-project', endpoint='your-end-point', )通过传入Table对象创建一个DataFrame对象。
from odps.df import DataFrame users = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_ml_100k_users'));您可以通过
dtypes属性查看这个DataFrame的字段及字段类型。print(users.dtypes)返回值
odps.Schema { user_id int64 age int64 sex string occupation string zip_code string }通过
head方法,您可以获取前N条数据并进行快速预览。print(users.head(10))返回值
user_id age sex occupation zip_code 0 1 24 M technician 85711 1 2 53 F other 94043 2 3 23 M writer 32067 3 4 24 M technician 43537 4 5 33 F other 15213 5 6 42 M executive 98101 6 7 57 M administrator 91344 7 8 36 M administrator 05201 8 9 29 M student 01002 9 10 53 M lawyer 90703如果您不需要看到所有字段,则可以进行如下操作:
从中筛选出一部分字段。
print(users[['user_id', 'age']].head(5))返回值
user_id age 0 1 24 1 2 53 2 3 23 3 4 24 4 5 33只做排除个别字段操作。
print(users.exclude('zip_code', 'age').head(5))返回值
user_id sex occupation 0 1 M technician 1 2 F other 2 3 M writer 3 4 M technician 4 5 F other排除掉一些字段,通过计算得到一些新的列。例如将
sex为M的置为True,否则为False,并取名为sex_bool。print(users.select(users.exclude('zip_code', 'sex'), sex_bool=users.sex == 'M').head(5))返回值
user_id age occupation sex_bool 0 1 24 technician True 1 2 53 other False 2 3 23 writer True 3 4 24 technician True 4 5 33 other False
查看男用户和女用户的个数。
print(users.groupby(users.sex).agg(count=users.count()))返回值
sex count 0 F 273 1 M 670将用户按职业划分,从高到低进行排序,查看人数最多的前10职业。
df = users.groupby('occupation').agg(count=users['occupation'].count()) df1 = df.sort(df['count'], ascending=False) print(df1.head(10))返回值
occupation count 0 student 196 1 other 105 2 educator 95 3 administrator 79 4 engineer 67 5 programmer 66 6 librarian 51 7 writer 45 8 executive 32 9 scientist 31或者通过
value_counts方法快速实现。该方法返回的行数受到options.df.odps.sort.limit的限制,详情请参见配置选项。df = users.occupation.value_counts()[:10] print(df.head(10))返回值
occupation count 0 student 196 1 other 105 2 educator 95 3 administrator 79 4 engineer 67 5 programmer 66 6 librarian 51 7 writer 45 8 executive 32 9 scientist 31使用
join将这三张表联合起来,然后保存为一张新的表pyodps_ml_100k_lens。movies = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_ml_100k_movies')) ratings = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_ml_100k_ratings')) o.delete_table('pyodps_ml_100k_lens', if_exists=True) lens = movies.join(ratings).join(users).persist('pyodps_ml_100k_lens') print(lens.dtypes)返回值
odps.Schema { movie_id int64 title string release_date string ideo_release_date string imdb_url string unknown int64 action int64 adventure int64 animation int64 children int64 comedy int64 crime int64 documentary int64 drama int64 fantasy int64 filmnoir int64 horror int64 musical int64 mystery int64 romance int64 scifi int64 thriller int64 war int64 western int64 user_id int64 rating int64 timestamp int64 age int64 sex string occupation string zip_code string }
Dataframe数据处理
请您首先下载鸢尾花数据集。本文使用DataWorks PyODPS节点功能,详情请参见开发PyODPS 3任务。
创建测试数据表 。
使用DataWorks表管理功能新建表:
选择编辑页面左上角DDL
 。
。输入建表语句如下,完成后提交表。
CREATE TABLE pyodps_iris ( sepallength double COMMENT '片长度(cm)', sepalwidth double COMMENT '片宽度(cm)', petallength double COMMENT '瓣长度(cm)', petalwidth double COMMENT '瓣宽度(cm)', name string COMMENT '种类' ) ;
上传测试数据 。
在新建表上单击右键,选择导入数据,单击下一步,上传您刚下载的数据集。
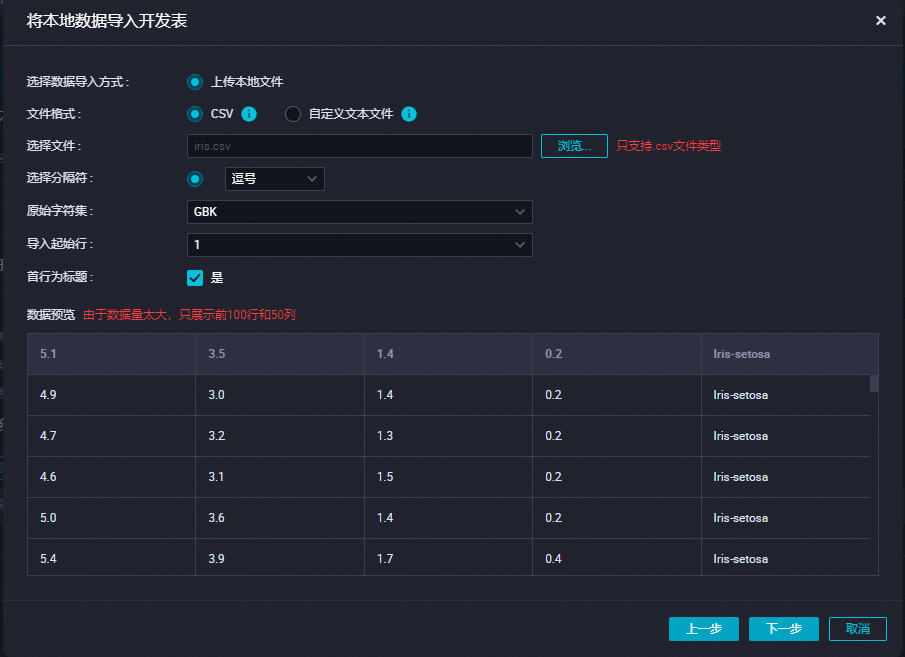
单击按位置匹配后导入数据。
打开相应的业务流程,右键单击MaxCompute,选择新建节点,选择PyODPS 3,新建一个PyODPS节点,用于存放和运行代码。
输入代码后,单击运行
 ,运行后可在下方运行日志处查看结果。代码详情如下。
,运行后可在下方运行日志处查看结果。代码详情如下。from odps import ODPS from odps.df import DataFrame, output import os # 确保 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID 环境变量设置为用户 Access Key ID, # ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET 环境变量设置为用户 Access Key Secret, # 不建议直接使用 Access Key ID / Access Key Secret 字符串 o = ODPS( os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID'), os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'), project='your-default-project', endpoint='your-end-point', ) # 从ODPS表创建DataFrame对象iris。 iris = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_iris')) print(iris.head(10)) # 打印iris部分内容。 print(iris.sepallength.head(5)) # 使用自定义函数求iris的两列之和。 print(iris.apply(lambda row: row.sepallength + row.sepalwidth, axis=1, reduce=True, types='float').rename('sepaladd').head(3)) # 指定函数的输出名称和类型。 @output(['iris_add', 'iris_sub'], ['float', 'float']) def handle(row): # 使用yield关键字可返回多行结果。 yield row.sepallength - row.sepalwidth, row.sepallength + row.sepalwidth yield row.petallength - row.petalwidth, row.petallength + row.petalwidth # 打印前5行结果,axis=1表示列的轴沿着水平的方向。 print(iris.apply(handle, axis=1).head(5))运行结果:
# print(iris.head(10)) sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth name 0 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa 1 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 Iris-setosa 2 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa 3 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa 4 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 Iris-setosa 5 4.6 3.4 1.4 0.3 Iris-setosa 6 5.0 3.4 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa 7 4.4 2.9 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa 8 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 Iris-setosa 9 5.4 3.7 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa # print(iris.sepallength.head(5)) sepallength 0 4.9 1 4.7 2 4.6 3 5.0 4 5.4 # print(iris.apply(lambda row: row.sepallength + row.sepalwidth, axis=1, reduce=True, types='float').rename('sepaladd').head(3)) sepaladd 0 7.9 1 7.9 2 7.7 # print(iris.apply(handle,axis=1).head(5)) iris_add iris_sub 0 1.9 7.9 1 1.2 1.6 2 1.5 7.9 3 1.1 1.5 4 1.5 7.7
