本文介绍了计划加速(PartitionedTable Scan)的功能背景、使用方法以及性能对比等内容。
背景
PolarDB PostgreSQL版(兼容Oracle)对分区表的分区数量没有限制。当分区超过2级时,分区数量便会成倍增加。
例如,一个分区表有两级分区,一级分区按照哈希分区,有100个分区;二级分区按照哈希分区,每个二级分区再次分成100个子分区。此时整个分区表共有10000个分区。此时如果对这个分区表进行查询,查询计划如下:
explain analyze select * from part_hash;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Append (cost=0.00..344500.00 rows=16300000 width=22)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash_sys0102 (cost=0.00..26.30 rows=1630 width=22)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash_sys0103 (cost=0.00..26.30 rows=1630 width=22)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash_sys0104 (cost=0.00..26.30 rows=1630 width=22)
...
...
...
-> Seq Scan on part_hash_sys10198 (cost=0.00..26.30 rows=1630 width=22)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash_sys10199 (cost=0.00..26.30 rows=1630 width=22)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash_sys10200 (cost=0.00..26.30 rows=1630 width=22)
Planning Time: 3183.644 ms
Execution Time: 633.779 ms
(10003 rows)
Total Memory: 216852KB从上述结果可以看到,查询过程比较缓慢。这是因为分区表在优化器中的原理可以简单理解为:首先对每个分区生成最优的Plan,然后使用Append算子把这些Plan并联起来作为分区表的最优Plan。如果分区表的分区数量较少,这个过程会很快,对于用户是无感知的;但是一旦达到一定规模的分区数,这个过程变得逐渐明显,用户在查询过程中感到分区表的查询相比于普通表尤为缓慢。
如上面的SQL中,表part_hash有10000个分区,它的Planning Time可以达到3秒左右,但普通表的查询Planning Time仅需0.1毫秒,达到了几百倍的差距。并且除了Planning Time上的差距,查询进程内存的占用也非常巨大,可能会引发OOM。
分区表的这个缺陷在使用连接查询时更加明显:
create table part_hash2 (a int, b int, c varchar(10))
PARTITION by HASH(a) SUBPARTITION by HASH (b) PARTITIONS 100 SUBPARTITIONS 100;
explain analyze select count(*) from part_hash a join part_hash2 b on a.a=b.b where b.c = '0001';
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Finalize Aggregate (cost=48970442.90..48970442.91 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=6466.854..6859.935 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Gather (cost=48970442.68..48970442.89 rows=2 width=8) (actual time=397.780..6859.902 rows=3 loops=1)
Workers Planned: 2
Workers Launched: 2
-> Partial Aggregate (cost=48969442.68..48969442.69 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=4.748..11.768 rows=1 loops=3)
-> Merge Join (cost=1403826.01..42177776.01 rows=2716666667 width=0) (actual time=4.736..11.756 rows=0 loops=3)
Merge Cond: (a.a = b.b)
-> Sort (cost=1093160.93..1110135.93 rows=6790000 width=4) (actual time=4.734..8.588 rows=0 loops=3)
Sort Key: a.a
Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 25kB
Worker 0: Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 25kB
Worker 1: Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 25kB
-> Parallel Append (cost=0.00..229832.35 rows=6790000 width=4) (actual time=4.665..8.518 rows=0 loops=3)
-> Parallel Seq Scan on part_hash_sys0102 a (cost=0.00..19.59 rows=959 width=4) (actual time=0.001..0.001 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Parallel Seq Scan on part_hash_sys0103 a_1 (cost=0.00..19.59 rows=959 width=4) (actual time=0.001..0.001 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Parallel Seq Scan on part_hash_sys0104 a_2 (cost=0.00..19.59 rows=959 width=4) (actual time=0.001..0.001 rows=0 loops=1)
...
-> Sort (cost=310665.08..310865.08 rows=80000 width=4) (never executed)
Sort Key: b.b
-> Append (cost=0.00..304150.00 rows=80000 width=4) (never executed)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash2_sys0102 b (cost=0.00..30.38 rows=8 width=4) (never executed)
Filter: ((c)::text = '0001'::text)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash2_sys0103 b_1 (cost=0.00..30.38 rows=8 width=4) (never executed)
Filter: ((c)::text = '0001'::text)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash2_sys0104 b_2 (cost=0.00..30.38 rows=8 width=4) (never executed)
Filter: ((c)::text = '0001'::text)
...
Planning Time: 221082.616 ms
Execution Time: 9500.148 ms
(30018 rows)
Total Memory: 679540KB因此我们可以看到分区表在进行全表查询时,因为没有指定任何限定条件,无法将查询集中在某个分区内,这导致在全表查询场景下,分区表所有的优势不再存在,比普通表更加低效。尽管我们可以通过分区剪枝使查询可以集中在少部分分区,但是对于一些OLAP场景,必须对整个分区表进行全表扫描。
概述
为了解决这个问题,提供了PartitionedTableScan算子。它是一个分区表的查询算子,比Append更加高效,可以明显降低Planning Time,且使用更少的内存,有效避免OOM。该算子用于解决分区表分区数量过多时,查询性能慢的问题。
下方展示了当使用PartitionedTableScan算子时,分别查询这两个SQL所用的Planning Time和内存。
explain analyze select * from part_hash;
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PartitionedTableScan on part_hash (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=22) (actual time=134.348..134.352 rows=0 loops=1)(Iteration partition number 10000)
Scan Partitions: part_hash_sys0102, part_hash_sys0103, ...part_hash_sys10198, part_hash_sys10199, part_hash_sys10200
-> Seq Scan on part_hash (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=22)
Planning Time: 293.778 ms
Execution Time: 384.202 ms
(5 rows)
Total Memory: 40276KB
explain analyze select count(*) from part_hash a join part_hash2 b on a.a=b.b where b.c = '0001';
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=2.02..2.03 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=152.322..152.326 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=0.00..2.02 rows=1 width=0) (actual time=152.308..152.311 rows=0 loops=1)
Join Filter: (a.a = b.b)
-> PartitionedTableScan on part_hash a (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=152.305..152.306 rows=0 loops=1)(Iteration partition number 10000)
Scan Partitions: part_hash_sys0102, part_hash_sys0103,, part_hash_sys10198, part_hash_sys10199, part_hash_sys10200
-> Seq Scan on part_hash a (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=4)
-> PartitionedTableScan on part_hash2 b (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=4) (never executed)
-> Seq Scan on part_hash2 b (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=4)
Filter: ((c)::text = '0001'::text)
Planning Time: 732.952 ms
Execution Time: 436.927 ms
(11 rows)
Total Memory: 68104KB可以看到,在本示例中,不管是Planning Time 还是内存Total Memory,使用PartitionedTableScan算子后都显著下降。具体数字对比示例如下表:
类型 |
|
|
Single Query Planning Time | 3183.644ms | 293.778ms |
Single Total Memory | 216852 KB | 40276 KB |
Join Query Planning Time | 221082.616ms | 732.952ms |
Join Total Memory | 679540 KB | 68104 KB |
使用限制
PolarDB PostgreSQL版(兼容Oracle)1.0和2.0都支持
PartitionedTableScan算子。且内核小版本需为V1.1.32及以上。PartitionedTableScan目前仅支持Select,不支持DML语句。PartitionedTableScan不支持分区连接。如果您开启了分区连接功能,将不会生成PartitionedTableScan计划。
PartitionedTable Scan功能仅适用于内核小版本为V1.1.32及以上的集群。若早于该内核小版本的存量集群需要使用该功能,请联系我们进行开启。
使用说明
为了更好的说明PartitionedTableScan功能,我们结合如下示例来进行介绍。
首先创建一张分区表。
CREATE TABLE prt1 (a int, b int, c varchar) PARTITION BY Hash(a) partitions 16;通过参数启用PartitionedTableScan
通过对参数polar_num_parts_for_partitionedscan的设置调整,可以开启或关闭PartitionedTableScan功能。
参数 | 取值范围 | 默认值 | 说明 |
polar_num_parts_for_partitionedscan | -1至INT_MAX | 64 | 表示 例如,当为默认值时,即表示当分区表的子分区数量大于64时,自动开启 该参数有如下两个特殊取值:
|
示例如下:
SET polar_num_parts_for_partitionedscan to -1;
explain select * from prt1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------
PartitionedTableScan on prt1 (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=40)
-> Seq Scan on prt1 (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=40)
(2 rows)使用HINT
使用HINT语法PARTEDSCAN(table alias),示例如下:
EXPLAIN select /*+PARTEDSCAN(prt1) */ select * from prt1;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------
PartitionedTableScan on prt1 (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=40)
-> Seq Scan on prt1 (cost=0.00..1.00 rows=1 width=40)
(2 rows)并行查询
支持分区表的并行查询,它能很好的处理大规模数据的查询。和Append一样,PartitionedTableScan也支持并行查询。但和Append不同的是,PartitionedTableScan的并行查询被称之为PartitionedTableScan Append,并行的方式只有两种:分区间并行和混合并行。
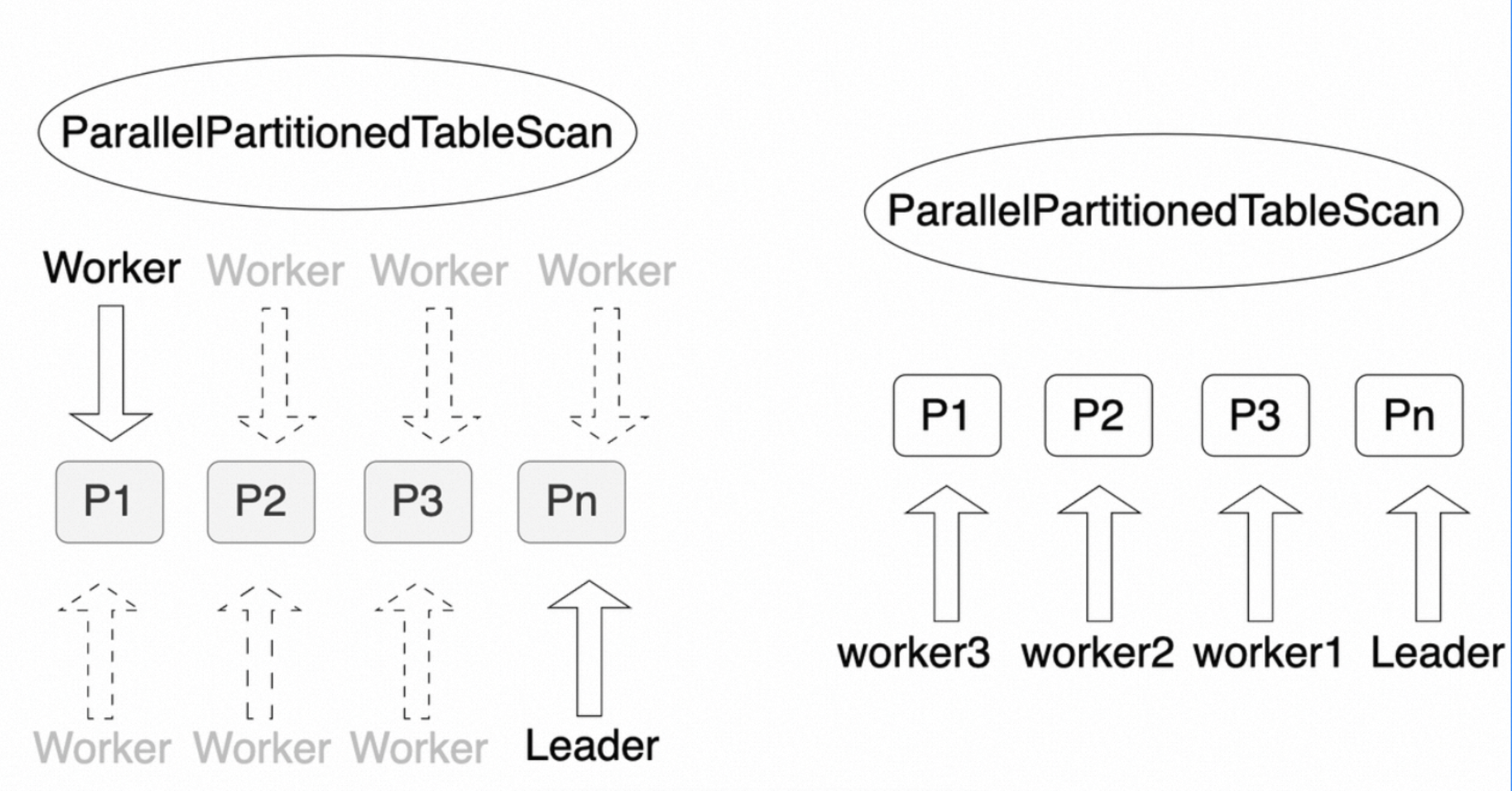
分区间并行
分区间并行是指每个worker查询一个分区,以实现多个worker并行查询整个分区表。
EXPLAIN (COSTS OFF) select /*+PARTEDSCAN(prt1) */ * from prt1;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------
Gather
Workers Planned: 4
-> Parallel PartitionedTableScan on prt1
-> Seq Scan on prt1
(4 rows)如上所示,整个分区表启动了4个并行的Worker(Workers Planned: 4),每个Worker负责查询一个分区。其中,明显的标志是有一个名为Parallel PartitionedTableScan的算子。
混合并行
混合并行是指分区间和分区内都可以并行执行,从而达到分区表整体的并行执行,这是并行度最高的一种并行查询。
EXPLAIN (COSTS OFF) select /*+PARTEDSCAN(prt1) */ * from prt1;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------
Gather
Workers Planned: 8
-> Parallel PartitionedTableScan on prt1
-> Parallel Seq Scan on prt1
(4 rows)如上所示,整个查询使用了8个worker进行并行查询(Workers Planned: 8),每个分区之间可以并行查询,每个分区内部也可以并行查询。其中,明显的标志是有一个名为Parallel PartitionedTableScan的算子。
以上两种并行方式都有自己的代价模型,优化器会选择最优的一种。
分区剪枝
PartitionedTableScan和Append一样,支持三个阶段的分区剪枝。关于分区剪枝的详细说明,请参见分区剪枝。
性能对比
PartitionedTableScan相比于Append更加高效。如下测试数据展示了PartitionedTableScan和Append的性能对比。
以下测试数据是开发环境测试出的临时数据,不是性能标准数据。不同配置、不同条件下测试出的数据可能不同。本测试的目的是根据单一变量原则,在环境配置一致的情况下,对比Append和PartitionedTableScan的性能差异。
如下为测试SQL:
explain select * from prt1 where b = 10;
explain select /*+PARTEDSCAN(prt1) */ * from prt1 where b = 10; 单条SQL的Planning Time
分区数量 | Append Planning Time | PartitionedTableScan Planning Time |
16 | 0.266ms | 0.067ms |
32 | 1.820ms | 0.258ms |
64 | 3.654ms | 0.402ms |
128 | 7.010ms | 0.664ms |
256 | 14.095ms | 1.247ms |
512 | 27.697ms | 2.328ms |
1024 | 73.176ms | 4.165ms |
Memory(单条SQL的内存使用量)
分区数量 | Append Memory | PartitionedTableScan Memory |
16 | 1,170 KB | 1,044 KB |
32 | 1,240 KB | 1,044 KB |
64 | 2,120 KB | 1,624 KB |
128 | 2,244 KB | 1,524 KB |
256 | 2,888 KB | 2,072 KB |
512 | 4,720 KB | 3,012 KB |
1024 | 8,236 KB | 5,280 KB |
QPS(Query per Second)
pgbench -i --scale=10
pgbench -c 64 -j 64 -n -T60
Query:
explain select * from prt1 where b = 10;
explain select /*+PARTEDSCAN(prt1) */ * from prt1 where b = 10; 分区数量 | Append QPS | PartitionedTableScan QPS |
16 | 25,318 | 93,950 |
32 | 10,906 | 61,879 |
64 | 5,281 | 30,839 |
128 | 2,195 | 16,684 |
256 | 920 | 8,372 |
512 | 92 | 3,708 |
1024 | 21 | 1,190 |
结论
从上面的PartitionedTableScan和Append的对比可以看出,PartitionedTableScan相比于Append随着分区数量增加时,性能提升明显。因此,如果您在业务中分区表分区数量较多且Planning Time很大时,我们建议您使用PartitionedTableScan进行一定程度的优化。
