本文介绍通过reindex方式,将ECS上自建Elasticsearch(简称ES)集群中的数据迁移至阿里云ES中,包括创建索引和迁移数据。
背景信息
通过reindex迁移数据,仅支持单可用区实例。如果您使用的是多可用区实例,建议采用如下方案将自建ES数据迁移至阿里云:
如果源端数据量较大,建议采用OSS快照方式。具体操作,请参见进阶版:通过OSS将自建ES集群迁移至阿里云ES。
如果需要对源端数据进行过滤,建议采用Logstash迁移方案。具体操作,请参见通过阿里云Logstash将自建Elasticsearch数据迁移至阿里云。
前提条件
您已完成以下操作:
创建单可用区的阿里云ES实例。
具体操作请参见创建阿里云Elasticsearch实例。
准备自建ES集群和待迁移的数据。
如果您还没有自建ES集群,建议您使用阿里云ECS进行搭建,具体操作步骤请参见安装并运行Elasticsearch。自建ES集群需要满足以下条件:
所在的ECS的网络类型必须是专有网络(不支持ClassicLink方式打通的ECS),且必须与阿里云ES在同一个专有网络下。
所在的ECS的安全组不能限制阿里云ES实例的各节点IP(Kibana控制台可查看各节点的IP),且要开启9200端口。
能够与阿里云ES实例连通。可在执行脚本的机器上,使用
curl -XGET http://<host>:9200命令验证。说明您可以通过任意一台机器执行文档中的脚本,前提是该机器可以同时访问自建ES和阿里云ES集群的9200端口。
使用限制
目前阿里云ES拥有基础管控(v2)架构以及云原生新管控(v3)架构两种部署模式,您可以通过实例基本信息中的管控部署模式进行辨别。

云原生新管控(v3)架构下的集群跨集群reindex需依赖Privatelink打通阿里云ES集群私网。您可以参见下表,依据您的业务场景选择解决方案进行处理。
使用场景 | ES集群所处网络架构 | 解决方案 |
阿里云ES集群间的数据迁移 | 两个ES集群均创建于基础管控(v2)架构下。 | reindex方式:阿里云ES间跨集群reindex。 |
其中一个ES集群创建于云原生新管控(v3)架构下。 说明 另一个ES集群可以创建于云原生新管控(v3)架构,也可以创建于基础管控(v2)架构。 |
| |
将ECS上自建的ES集群中的数据迁移至阿里云ES集群中 | 阿里云ES集群创建于基础管控(v2)架构下。 | reindex方式:通过reindex将自建ES数据迁移至阿里云。 |
阿里云ES集群创建于云原生新管控(v3)架构下。 | reindex方式:通过实例私网打通将自建Elasticsearch数据迁移至阿里云。 |
注意事项
2020年10月,阿里云Elasticsearch对网络架构进行了调整。2020年10月之前为旧网络架构,2020年10月及之后为新网络架构。新网络架构下的实例不支持与旧网络架构下的实例进行跨集群reindex、跨集群搜索、跨集群复制等实例互通操作。如果需要进行互通,需要确保实例创建在同一网络架构下。对于华北3(张家口)和海外地域,由于网络架构调整时间不确定,因此需要联系阿里云Elasticsearch技术支持,校验网络是否可以互通。
云原生新管控(v3)架构下,阿里云ES实例部署在阿里云服务账号下的VPC中,不支持访问其他网络环境下的资源;基础管控(v2)架构下,阿里云ES部署在用户VPC中,网络访问不受影响。
为保证数据迁移前后一致,建议上游业务停止自建ES集群的数据写入更新操作,确保读操作正常进行。迁移完成后,直接切换到阿里云ES集群进行读写操作。如果不停止写操作,建议通过脚本设置循环任务减少停写服务时间,具体请参见步骤四:迁移数据中的《数据量大、无删除操作、有更新时间》章节。
当使用域名访问自建ES或阿里云ES集群时,不允许通过
http://host:port/path这种带path的形式访问。
操作流程
步骤一:获取终端域名(可选)
如果您创建的阿里云ES处于云原生新管控(v3)架构下,需要借助PrivateLink,打通ECS上自建的ES集群所处的网络与阿里云服务账号的网络,获取终端域名,为后续配置做准备。具体操作,请参见配置实例私网连接。
步骤二:创建目标端索引
参考自建ES集群中需要迁移的索引配置,提前在阿里云ES集群中创建索引。或者为阿里云ES集群开启自动创建索引功能(不建议)。
以Python2为例,使用如下脚本,在阿里云ES集群中批量创建自建ES集群中需要迁移的索引。默认新创建的索引副本数为0。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# 文件名:indiceCreate.py
import sys
import base64
import time
import httplib
import json
## 自建Elasticsearch集群host。
oldClusterHost = "old-cluster.com"
## 自建Elasticsearch集群用户名,可为空。
oldClusterUserName = "old-username"
## 自建Elasticsearch集群密码,可为空。
oldClusterPassword = "old-password"
## 阿里云Elasticsearch集群host,可在阿里云Elasticsearch实例的基本信息页面获取。
newClusterHost = "new-cluster.com"
## 阿里云Elasticsearch集群用户名。
newClusterUser = "elastic"
## 阿里云Elasticsearch集群密码。
newClusterPassword = "new-password"
DEFAULT_REPLICAS = 0
def httpRequest(method, host, endpoint, params="", username="", password=""):
conn = httplib.HTTPConnection(host)
headers = {}
if (username != "") :
'Hello {name}, your age is {age} !'.format(name = 'Tom', age = '20')
base64string = base64.encodestring('{username}:{password}'.format(username = username, password = password)).replace('\n', '')
headers["Authorization"] = "Basic %s" % base64string;
if "GET" == method:
headers["Content-Type"] = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, headers=headers)
else :
headers["Content-Type"] = "application/json"
conn.request(method=method, url=endpoint, body=params, headers=headers)
response = conn.getresponse()
res = response.read()
return res
def httpGet(host, endpoint, username="", password=""):
return httpRequest("GET", host, endpoint, "", username, password)
def httpPost(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""):
return httpRequest("POST", host, endpoint, params, username, password)
def httpPut(host, endpoint, params, username="", password=""):
return httpRequest("PUT", host, endpoint, params, username, password)
def getIndices(host, username="", password=""):
endpoint = "/_cat/indices"
indicesResult = httpGet(oldClusterHost, endpoint, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
indicesList = indicesResult.split("\n")
indexList = []
for indices in indicesList:
if (indices.find("open") > 0):
indexList.append(indices.split()[2])
return indexList
def getSettings(index, host, username="", password=""):
endpoint = "/" + index + "/_settings"
indexSettings = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password)
print index + " 原始settings如下:\n" + indexSettings
settingsDict = json.loads(indexSettings)
## 分片数默认和自建Elasticsearch集群索引保持一致。
number_of_shards = settingsDict[index]["settings"]["index"]["number_of_shards"]
## 副本数默认为0。
number_of_replicas = DEFAULT_REPLICAS
newSetting = "\"settings\": {\"number_of_shards\": %s, \"number_of_replicas\": %s}" % (number_of_shards, number_of_replicas)
return newSetting
def getMapping(index, host, username="", password=""):
endpoint = "/" + index + "/_mapping"
indexMapping = httpGet(host, endpoint, username, password)
print index + " 原始mapping如下:\n" + indexMapping
mappingDict = json.loads(indexMapping)
mappings = json.dumps(mappingDict[index]["mappings"])
newMapping = "\"mappings\" : " + mappings
return newMapping
def createIndexStatement(oldIndexName):
settingStr = getSettings(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
mappingStr = getMapping(oldIndexName, oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
createstatement = "{\n" + str(settingStr) + ",\n" + str(mappingStr) + "\n}"
return createstatement
def createIndex(oldIndexName, newIndexName=""):
if (newIndexName == "") :
newIndexName = oldIndexName
createstatement = createIndexStatement(oldIndexName)
print "新索引 " + newIndexName + " 的setting和mapping如下:\n" + createstatement
endpoint = "/" + newIndexName
createResult = httpPut(newClusterHost, endpoint, createstatement, newClusterUser, newClusterPassword)
print "新索引 " + newIndexName + " 创建结果:" + createResult
## main
indexList = getIndices(oldClusterHost, oldClusterUserName, oldClusterPassword)
systemIndex = []
for index in indexList:
if (index.startswith(".")):
systemIndex.append(index)
else :
createIndex(index, index)
if (len(systemIndex) > 0) :
for index in systemIndex:
print index + " 或许是系统索引,不会重新创建,如有需要,请单独处理~"步骤三:配置reindex白名单
在左侧导航栏,单击Elasticsearch实例。
进入目标实例。
在顶部菜单栏处,选择资源组和地域。
在Elasticsearch实例中单击目标实例ID。
在左侧导航栏,选择。
在YML文件配置区域,单击右侧的修改配置。
在YML文件配置面板,修改其他Configure配置,配置reindex白名单。
配置示例如下。
reindex.remote.whitelist: ["10.0.xx.xx:9200","10.0.xx.xx:9200","10.0.xx.xx:9200","10.15.xx.xx:9200","10.15.xx.xx:9200","10.15.xx.xx:9200"]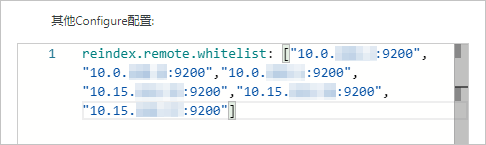
在配置reindex白名单时,需要通过reindex.remote.whitelist参数,设置自建ES集群的访问地址,将其添加到阿里云ES集群的远程访问白名单中。阿里云ES集群的网络架构不同,配置规则也不同,具体如下:
基础管控(v2)架构下:需要配置为host和port的组合,并使用逗号分隔多个主机配置。例如:otherhost:9200,another:9200,127.0.10.**:9200,localhost:**,不识别协议信息。
云原生新管控(v3)架构下:需要配置为实例对应的终端节点域名和port的组合。例如:ep-bp1hfkx7coy8lvu4****-cn-hangzhou-i.epsrv-bp1zczi0fgoc5qtv****.cn-hangzhou.privatelink.aliyuncs.com:9200。
说明更多参数说明请参见配置YML参数。
选中该操作会重启实例,请确认后操作。,单击确认。
确定后,Elasticsearch实例会重启。重启过程中,可在任务列表查看进度。重启成功后,即可完成配置。
步骤四:迁移数据
本文以基础管控(v2)架构下的实例为例,提供了以下三种数据迁移的方式,请根据迁移的数据量大小以及实际业务情况,选择合适的方式迁移数据。
数据量小
使用如下脚本。
#!/bin/bash
# file:reindex.sh
indexName="您的索引名"
newClusterUser="阿里云Elasticsearch集群用户名"
newClusterPass="阿里云Elasticsearch集群密码"
newClusterHost="阿里云Elasticsearch集群host"
oldClusterUser="自建Elasticsearch集群用户名"
oldClusterPass="自建Elasticsearch集群密码"
# 自建Elasticsearch集群host必须是[scheme]://[host]:[port],例如http://10.37.*.*:9200。
oldClusterHost="自建Elasticsearch集群host"
curl -u ${newClusterUser}:${newClusterPass} -XPOST "http://${newClusterHost}/_reindex?pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d'{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "'${oldClusterHost}'",
"username": "'${oldClusterUser}'",
"password": "'${oldClusterPass}'"
},
"index": "'${indexName}'",
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "'${indexName}'"
}
}'数据量大、无删除操作、有更新时间
数据量较大且无删除操作时,可以使用滚动迁移的方式,减少停止写服务的时间。滚动迁移需要有一个类似于更新时间的字段代表新数据的写时序。在数据迁移完成后,先停止业务写操作,待reindex使用最近一次更新时间快速执行一次更新后,将读写业务切换到阿里云ES集群。
#!/bin/bash
# file: circleReindex.sh
# CONTROLLING STARTUP:
# 这是通过reindex操作远程重建索引的脚本,要求:
# 1. 阿里云Elasticsearch集群已经创建完索引,或者支持自动创建和动态映射。
# 2. 阿里云Elasticsearch集群必须在yml里配置IP白名单,例如reindex.remote.whitelist: 172.16.**.**:9200。
# 3. host必须是[scheme]://[host]:[port]。
USAGE="Usage: sh circleReindex.sh <count>
count: 执行次数,多次(负数为循环)增量执行或者单次执行
Example:
sh circleReindex.sh 1
sh circleReindex.sh 5
sh circleReindex.sh -1"
indexName="您的索引名"
newClusterUser="阿里云Elasticsearch集群用户名"
newClusterPass="阿里云Elasticsearch集群密码"
oldClusterUser="自建Elasticsearch集群用户名"
oldClusterPass="自建Elasticsearch集群密码"
## http://myescluster.com
newClusterHost="阿里云Elasticsearch集群host"
# 自建Elasticsearch集群host必须是[scheme]://[host]:[port],例如http://10.37.*.*:9200。
oldClusterHost="自建Elasticsearch集群host"
timeField="更新时间字段"
reindexTimes=0
lastTimestamp=0
curTimestamp=`date +%s`
hasError=false
function reIndexOP() {
reindexTimes=$[${reindexTimes} + 1]
curTimestamp=`date +%s`
ret=`curl -u ${newClusterUser}:${newClusterPass} -XPOST "${newClusterHost}/_reindex?pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "'${oldClusterHost}'",
"username": "'${oldClusterUser}'",
"password": "'${oldClusterPass}'"
},
"index": "'${indexName}'",
"query": {
"range" : {
"'${timeField}'" : {
"gte" : '${lastTimestamp}',
"lt" : '${curTimestamp}'
}
}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "'${indexName}'"
}
}'`
lastTimestamp=${curTimestamp}
echo "第${reindexTimes}次reIndex,本次更新截止时间 ${lastTimestamp} 结果:${ret}"
if [[ ${ret} == *error* ]]; then
hasError=true
echo "本次执行异常,中断后续执行操作~~,请检查"
fi
}
function start() {
## 负数就不停循环执行
if [[ $1 -lt 0 ]]; then
while :
do
reIndexOP
done
elif [[ $1 -gt 0 ]]; then
k=0
while [[ k -lt $1 ]] && [[ ${hasError} == false ]]; do
reIndexOP
let ++k
done
fi
}
## main
if [ $# -lt 1 ]; then
echo "$USAGE"
exit 1
fi
echo "开始执行索引 ${indexName} 的 ReIndex操作"
start $1
echo "总共执行 ${reindexTimes} 次 reIndex 操作"数据量大、无删除操作、无更新时间
当数据量较大,且索引的Mapping中没有定义更新时间的字段时,需要由上游业务修改代码添加更新时间的字段。添加完成后可以先将历史数据迁移完,然后再使用上述第二种方案操作。
#!/bin/bash
# file:miss.sh
indexName="您的索引名"
newClusterUser="阿里云Elasticsearch集群用户名"
newClusterPass="阿里云Elasticsearch集群密码"
newClusterHost="阿里云Elasticsearch集群host"
oldClusterUser="自建Elasticsearch集群用户名"
oldClusterPass="自建Elasticsearch集群密码"
# 自建Elasticsearch集群host必须是[scheme]://[host]:[port],例如http://10.37.*.*:9200
oldClusterHost="自建Elasticsearch集群host"
timeField="updatetime"
curl -u ${newClusterUser}:${newClusterPass} -XPOST "http://${newClusterHost}/_reindex?pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"source": {
"remote": {
"host": "'${oldClusterHost}'",
"username": "'${oldClusterUser}'",
"password": "'${oldClusterPass}'"
},
"index": "'${indexName}'",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"exists": {
"field": "'${timeField}'"
}
}
}
}
},
"dest": {
"index": "'${indexName}'"
}
}'常见问题
问题:执行curl命令时,提示
{"error":"Content-Type header [application/x-www-form-urlencoded] is not supported","status":406}。解决方法:在curl命令中,添加
-H "Content-Type: application/json"脚本重试。// 获取自建Elasticsearch集群中所有索引信息,如果没有权限可去掉"-u user:pass"参数,oldClusterHost为自建Elasticsearch集群的host,注意替换。 curl -u user:pass -XGET http://oldClusterHost/_cat/indices | awk '{print $3}' // 参考上面返回的索引列表,获取需要迁移的指定用户索引的setting和mapping,注意替换indexName为要查询的用户索引名。 curl -u user:pass -XGET http://oldClusterHost/indexName/_settings,_mapping?pretty=true // 参考上面获取到的对应索引的_settings和_mapping信息,在阿里云Elasticsearch集群中创建对应索引,索引副本数可以先设置为0,用于加快数据同步速度,数据迁移完成后再重置副本数为1。 //其中newClusterHost是阿里云Elasticsearch集群的host,testindex是已经创建的索引名,testtype是对应索引的type。 curl -u user:pass -XPUT http://<newClusterHost>/<testindex> -d '{ "testindex" : { "settings" : { "number_of_shards" : "5", //假设自建Elasticsearch集群中对应索引的shard数是5个。 "number_of_replicas" : "0" //设置索引副本为0。 } }, "mappings" : { //假设自建Elasticsearch集群中对应索引的mappings配置如下。 "testtype" : { "properties" : { "uid" : { "type" : "long" }, "name" : { "type" : "text" }, "create_time" : { "type" : "long" } } } } } }'问题:单索引数据量比较大,数据同步速度比较慢时,如何处理?
解决方法:
由于reindex功能的底层实现原理是通过scroll方式实现的,所以您可以适当调大scroll size的大小或配置scroll slice,借助scroll并行化机制提升效率。详情请参见reindex API。
如果源端数据量较大,建议采用OSS快照方式。详情请参见进阶版:通过OSS将自建ES集群迁移至阿里云ES。
如果单索引数据量比较大,可以在迁移前将目标索引的副本数设置为0,刷新时间设置为-1,以加快数据同步速度。待数据迁移完成后,再修改回来。
// 迁移索引数据前可以先将索引副本数设为0,不刷新,用于加快数据迁移速度。 curl -u user:password -XPUT 'http://<host:port>/indexName/_settings' -d' { "number_of_replicas" : 0, "refresh_interval" : "-1" }' // 索引数据迁移完成后,可以重置索引副本数为1,刷新时间1s(1s是默认值)。 curl -u user:password -XPUT 'http://<host:port>/indexName/_settings' -d' { "number_of_replicas" : 1, "refresh_interval" : "1s" }'
