Hologres从V2.0版本开始支持Runtime Filter,在多表Join场景下自动优化Join过程的过滤行为,提升Join的查询性能。本文为您介绍在Hologres中Runtime Filter的使用。
背景信息
应用场景
Hologres从V2.0版本开始支持Runtime Filter,通常应用在多表(两表及以上)Join的Hash Join场景,尤其是大表Join小表的场景中,无需手动设置,优化器和执行引擎会在查询时自动优化Join过程的过滤行为,从而降低I/O开销,以提升Join的查询性能。
原理介绍
在了解Runtime Filter原理之前,需先了解Join过程。两个表Join的SQL示例如下:
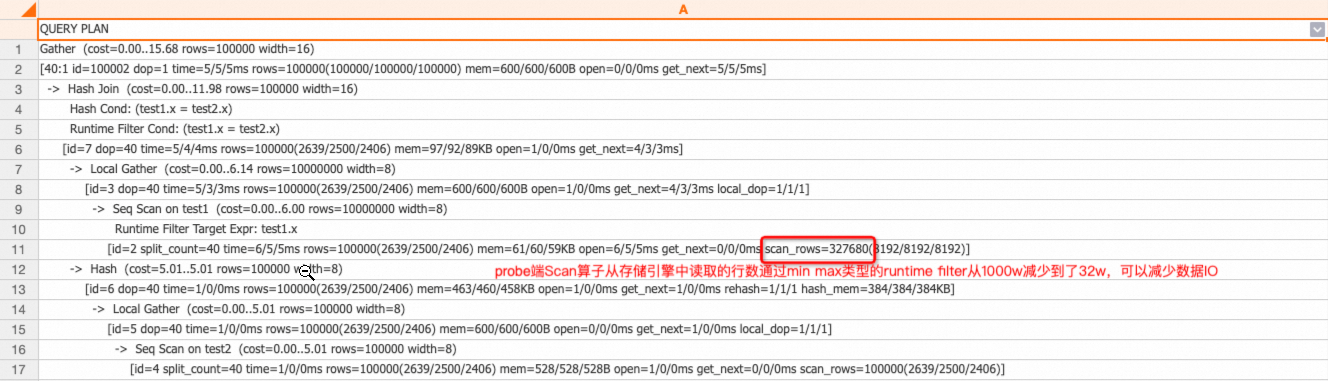
select * from test1 join test2 on test1.x = test2.x;其对应的执行计划如下。

如上执行计划,两个表Join时,会通过test2表构建Hash表,然后匹配test1表的数据,最后返回结果。在这个过程中,Join时会涉及到两个名词:
build端:两表(或者子查询)做Hash Join时,其中一张表(子查询)的数据会构建成Hash表,这一部分称为build端,对应计划里的Hash节点。
probe端:Hash Join的另一边,主要是读取数据然后和build端的Hash表进行匹配,这一部分称为probe端。
通常来说,在执行计划正确的情况下,小表是build端,大表是probe端。
Runtime Filter的原理就是在HashJoin过程中,利用build端的数据分布,生成一个轻量的过滤器(filter),发送给probe端,对probe端的数据进行裁剪,从而减少probe端真正参与Hash Join以及网络传输的数据量,以此来提升Hash Join性能。
因此Runtime Filter更适用于大小表Join,且表数据量相差较大的场景,性能将会比普通Join有更多的提升。
使用限制和触发条件
使用限制
仅Hologres V2.0及以上版本支持Runtime Filter。
仅支持Join条件中只有一个字段,如果有多个字段将不会触发Runtime Filter。从Hologres V2.1版本开始,Runtime Filter支持多个字段Join,如果多个Join字段满足触发条件,也会触发Runtime Filter。
仅4.0及以上版本支持 TopN Runtime Filter,用以提升单表 TopN 计算的场景的性能
触发条件
Hologres本身支持高性能的Join,因此Runtime Filter会根据查询条件在底层自动触发,但是需要SQL满足下述所有条件才能触发:
probe端的数据量在100000行及以上。
扫描的数据量比例:
build端 / probe端 <= 0.1(比例越小,越容易触发Runtime Filter)。Join出的数据量比例:
build端 / probe端 <= 0.1(比例越小,越容易触发Runtime Filter)。
Runtime Filter的类型
可以根据以下两个维度对Runtime Filter进行分类。
按照Hash Join的probe端是否需要进行Shuffle,可分为Local和Global类型。
Local类型:Hologres V2.0及以上版本支持。当Hash Join的probe端不需要Shuffle时,build端数据有如下三种情况,均可以使用Local类型的Runtime Filter:
build端和probe端的Join Key是同一种分布方式。
build端数据broadcast给probe端。
build端数据按照probe端数据的分布方式Shuffle给Probe端。
Global类型:Hologres V2.2及以上版本支持。当probe端数据需要Shuffle时,Runtime Filter需要合并后才可以使用,这种情况需要使用Global类型的Runtime Filter。
Local类型的Runtime Filer仅可能减少数据扫描量以及参与Hash Join计算的数据量,Global类型的Runtime Filter由于probe端数据会Shuffle,在数据Shuffle之前做过滤还可以减少数据的网络传输量。类型都无需手动指定,引擎会自适应。
按照Filter类型,可分为Bloom Filter、In Filter和MinMAX Filter。
Bloom Filter:Hologres V2.0及以上版本支持。Bloom Filter具有一定假阳性,导致少过滤一些数据,但其应用范围广,在build端数据量较多是仍能有较高的过滤效率,提升查询性能。
In Filter:Hologres V2.0及以上版本支持。In Filter在build端数据NDV(Number of Distinct Value,列的非重复值的个数)较小时使用,其会使用build端数据构建一个HashSet发送给probe端进行过滤,In Filter的优势是可以过滤所有应该过滤的数据,且可以和Bitmap索引结合使用。
MinMAX Filter:Hologres V2.0及以上版本支持。MinMAX Filter会根据build端数据得到最大值和最小值,发送给probe端做过滤,其优势为可能根据元数据信息直接过滤掉文件或一个Batch的数据,减少I/O成本。
三种Filter类型无需您手动指定,Hologres会根据运行时Join情况自适应使用各种类型的Filter。
验证Runtime Filter
如下示例帮助您更好地理解Runtime Filter。
示例1:Join条件中只有1列,使用Local类型Runtime Filter
示例代码:
begin; create table test1(x int, y int); call set_table_property('test1', 'distribution_key', 'x'); create table test2(x int, y int); call set_table_property('test2', 'distribution_key', 'x'); end; insert into test1 select t, t from generate_series(1, 100000) t; insert into test2 select t, t from generate_series(1, 1000) t; analyze test1; analyze test2; explain analyze select * from test1 join test2 on test1.x = test2.x;执行计划:

test2表只有1000行,test1表有100000行,build端和probe端的数据量比例是0.01,小于0.1,且Join出来的数据量build端和probe端比例是0.01,小于0.1,满足Runtime Filter的默认触发条件,因此引擎会自动使用Runtime Filter。probe端的
test1表有Runtime Filter Target Expr节点,表示probe端使用了Runtime Filter下推。probe端的scan_rows代表从存储中读取的数据,有100000行,rows代表使用Runtime Filter过滤后,scan算子的行数,为1000行,可以从这两个数据上看Runtime Filter的过滤效果。
示例2:Join条件中有多列(Hologres V2.1版本支持),使用Local类型Runtime Filter
示例代码:
drop table if exists test1, test2; begin; create table test1(x int, y int); create table test2(x int, y int); end; insert into test1 select t, t from generate_series(1, 1000000) t; insert into test2 select t, t from generate_series(1, 1000) t; analyze test1; analyze test2; explain analyze select * from test1 join test2 on test1.x = test2.x and test1.y = test2.y;执行计划:

Join条件有多列,Runtime Filter也生成了多列。
build端broadcast,可以使用Local类型的Runtime Filter。
示例3:Global类型Runtime Filter支持Shuffle Join(Hologres V2.2版本支持)
示例代码:
SET hg_experimental_enable_result_cache = OFF; drop table if exists test1, test2; begin; create table test1(x int, y int); create table test2(x int, y int); end; insert into test1 select t, t from generate_series(1, 100000) t; insert into test2 select t, t from generate_series(1, 1000) t; analyze test1; analyze test2; explain analyze select * from test1 join test2 on test1.x = test2.x;执行计划:
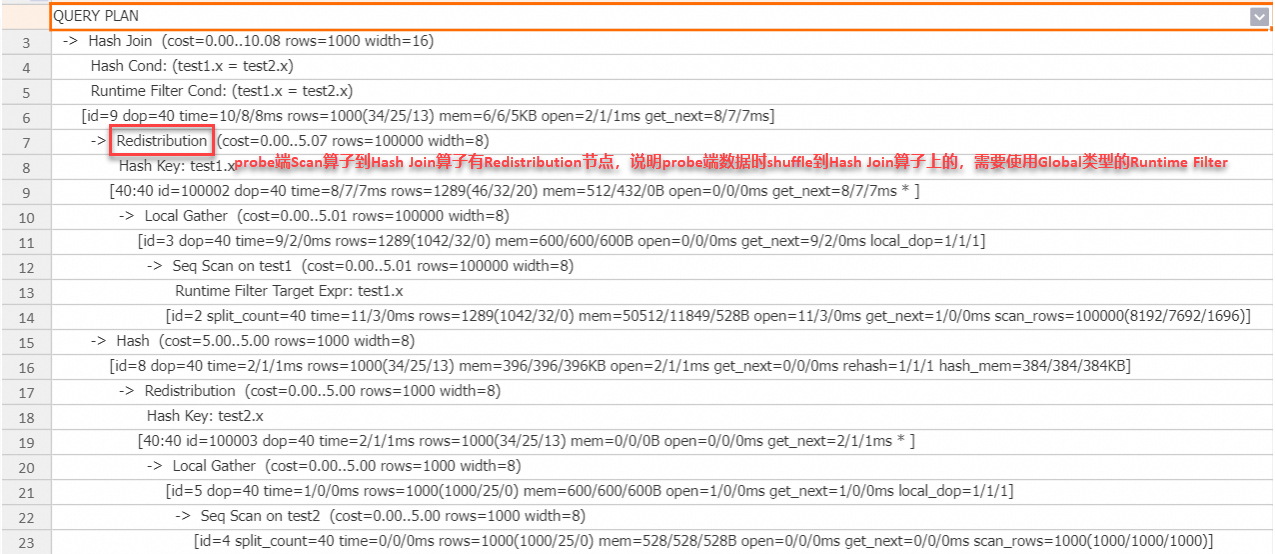
从上述执行计划可以看出,probe端数据被Shuffle到Hash Join算子,引擎会自动使用Global Runtime Filter来加速查询。
示例4:In类型的Filter结合bitmap索引(Hologres V2.2版本支持)
示例代码:
set hg_experimental_enable_result_cache=off; drop table if exists test1, test2; begin; create table test1(x text, y text); call set_table_property('test1', 'distribution_key', 'x'); call set_table_property('test1', 'bitmap_columns', 'x'); call set_table_property('test1', 'dictionary_encoding_columns', ''); create table test2(x text, y text); call set_table_property('test2', 'distribution_key', 'x'); end; insert into test1 select t::text, t::text from generate_series(1, 10000000) t; insert into test2 select t::text, t::text from generate_series(1, 50) t; analyze test1; analyze test2; explain analyze select * from test1 join test2 on test1.x = test2.x;执行计划:
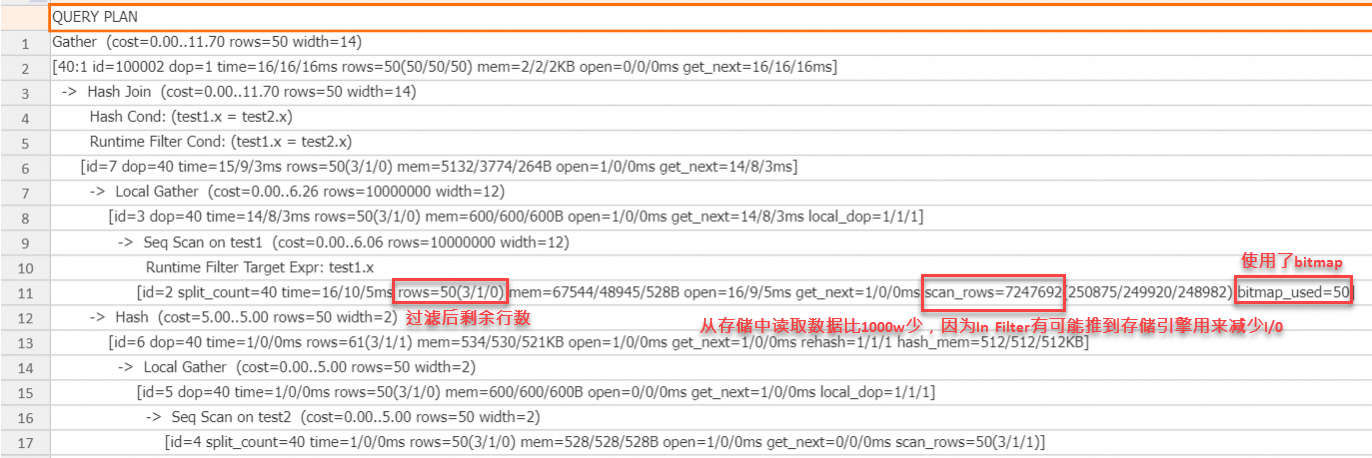
从上述执行计划可以看出,在probe端的scan算子上,使用了bitmap,因为In Filter可以精确过滤,因此过滤后还剩50行,scan算子中的scan_rows为700多万,比原始行数1000万少,这是因为In Filter可以推到存储引擎,有可能减少I/O成本,最终结果是从存储引擎中读取的数据变少了,In类型的Runtime Filter结合bitmap通常在Join Key为STRING类型时,有明显作用。
示例5:MinMax类型的Filter减少I/O(Hologres V2.2版本支持)
示例代码:
set hg_experimental_enable_result_cache=off; drop table if exists test1, test2; begin; create table test1(x int, y int); call set_table_property('test1', 'distribution_key', 'x'); create table test2(x int, y int); call set_table_property('test2', 'distribution_key', 'x'); end; insert into test1 select t::int, t::int from generate_series(1, 10000000) t; insert into test2 select t::int, t::int from generate_series(1, 100000) t; analyze test1; analyze test2; explain analyze select * from test1 join test2 on test1.x = test2.x;执行计划:

从上述执行计划可以看出,probe端scan算子从存储引擎读取的行数为32万多,比原始行数1000万少了很多,这是因为Runtime Filter被下推到存储引擎,利用一个batch数据的meta信息整批过滤数据,有可能大量减少I/O成本。通常在Join Key为数值类型,且build端值域范围比probe端的值域范围小时,有明显效果。
示例6:TopN Runtime Filter(Hologres V4.0版本支持)
在 Hologres 中,数据是以分块流式的方式进行处理的。因此,当 SQL 语句中包含 topN 算子时,Hologres 并不会计算所有结果,而是会生成一个动态的 Filter 来提前对数据进行过滤。
以下列SQL语句为例:
select o_orderkey from orders order by o_orderdate limit 5;此 SQL 语句的执行计划如下:
QUERY PLAN
Limit (cost=0.00..116554.70 rows=0 width=8)
-> Sort (cost=0.00..116554.70 rows=100 width=12)
Sort Key: o_orderdate
[id=6 dop=1 time=317/317/317ms rows=5(5/5/5) mem=1/1/1KB open=317/317/317ms get_next=0/0/0ms]
-> Gather (cost=0.00..116554.25 rows=100 width=12)
[20:1 id=100002 dop=1 time=317/317/317ms rows=100(100/100/100) mem=6/6/6KB open=0/0/0ms get_next=317/317/317ms * ]
-> Limit (cost=0.00..116554.25 rows=0 width=12)
-> Sort (cost=0.00..116554.25 rows=150000000 width=12)
Sort Key: o_orderdate
Runtime Filter Sort Column: o_orderdate
[id=3 dop=20 time=318/282/258ms rows=100(5/5/5) mem=96/96/96KB open=318/282/258ms get_next=1/0/0ms]
-> Local Gather (cost=0.00..9.59 rows=150000000 width=12)
[id=2 dop=20 time=316/280/256ms rows=1372205(68691/68610/68498) mem=0/0/0B open=0/0/0ms get_next=316/280/256ms local_dop=1/1/1 * ]
-> Seq Scan on orders (cost=0.00..8.24 rows=150000000 width=12)
Runtime Filter Target Expr: o_orderdate
[id=1 split_count=20 time=286/249/222ms rows=1372205(68691/68610/68498) mem=179/179/179KB open=0/0/0ms get_next=286/249/222ms physical_reads=27074(1426/1353/1294) scan_rows=144867963(7324934/7243398/7172304)]
Query id:[1001003033996040311]
QE version: 2.0
Query Queue: init_warehouse.default_queue
======================cost======================
Total cost:[343] ms
Optimizer cost:[13] ms
Build execution plan cost:[0] ms
Init execution plan cost:[6] ms
Start query cost:[6] ms
- Queue cost: [0] ms
- Wait schema cost:[0] ms
- Lock query cost:[0] ms
- Create dataset reader cost:[0] ms
- Create split reader cost:[0] ms
Get result cost:[318] ms
- Get the first block cost:[318] ms
====================resource====================
Memory: total 7 MB. Worker stats: max 3 MB, avg 3 MB, min 3 MB, max memory worker id: 189*****.
CPU time: total 5167 ms. Worker stats: max 2610 ms, avg 2583 ms, min 2557 ms, max CPU time worker id: 189*****.
DAG CPU time stats: max 5165 ms, avg 2582 ms, min 0 ms, cnt 2, max CPU time dag id: 1.
Fragment CPU time stats: max 5137 ms, avg 1721 ms, min 0 ms, cnt 3, max CPU time fragment id: 2.
Ec wait time: total 90 ms. Worker stats: max 46 ms, max(max) 2 ms, avg 45 ms, min 44 ms, max ec wait time worker id: 189*****, max(max) ec wait time worker id: 189*****.
Physical read bytes: total 799 MB. Worker stats: max 400 MB, avg 399 MB, min 399 MB, max physical read bytes worker id: 189*****.
Read bytes: total 898 MB. Worker stats: max 450 MB, avg 449 MB, min 448 MB, max read bytes worker id: 189*****.
DAG instance count: total 3. Worker stats: max 2, avg 1, min 1, max DAG instance count worker id: 189*****.
Fragment instance count: total 41. Worker stats: max 21, avg 20, min 20, max fragment instance count worker id: 189*****.没有 TopN Filter 时,Scan 节点读取 orders 表的每个数据块,并将它们传给 TopN 节点。TopN 节点用堆排序维护当前已见数据中排名前 5 的行。
例如:
每个数据块约含 8192 行。处理完第一个块后,TopN 就知道该块中第 5 名的 o_orderdate。假设它是 1995-01-01。
Scan 节点在读第二个块时,就用 1995-01-01 作过滤条件。它只发送 o_orderdate ≤ 1995-01-01 的行给 TopN。阈值会动态更新。如果第二个块中第 5 名的 o_orderdate 更小,TopN 就用这个新值替换旧阈值。
用 EXPLAIN 命令可查看优化器生成的 TopN Runtime Filter。
-> Limit (cost=0.00..116554.25 rows=0 width=12)
-> Sort (cost=0.00..116554.25 rows=150000000 width=12)
Sort Key: o_orderdate
Runtime Filter Sort Column: o_orderdate
[id=3 dop=20 time=318/282/258ms rows=100(5/5/5) mem=96/96/96KB open=318/282/258ms get_next=1/0/0ms]如上述例子所示:TopN 节点上会显示 Runtime Filter Sort Column,表示这个 TopN 节点会产生一个 TopN Runtime Filter。