本文为您介绍Python SDK中DataFrame相关的典型场景操作示例。
DataFrame
PyODPS提供了DataFrame API,它提供了类似Pandas的接口,但是能充分利用MaxCompute的计算能力。完整的DataFrame文档请参见DataFrame。
假设已经存在三张表,分别是pyodps_ml_100k_movies(电影相关的数据)、pyodps_ml_100k_users(用户相关的数据)和pyodps_ml_100k_ratings(评分有关的数据)。
首先创建MaxCompute的入口对象。
import os from odps import ODPS # 确保 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID 环境变量设置为用户 Access Key ID, # ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET 环境变量设置为用户 Access Key Secret, # 不建议直接使用 Access Key ID / Access Key Secret 字符串 o = ODPS( os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID'), os.getenv('ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'), project='your-default-project', endpoint='your-end-point', )传入Table对象,创建DataFrame对象users。
from odps.df import DataFrame users = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_ml_100k_users'))对DataFrame对象可以执行如下操作:
通过dtypes属性可以查看DataFrame的字段和类型,如下所示。
users.dtypes通过head方法,可以获取前N条数据,方便快速预览数据。
users.head(10)返回结果如下。
-
user_id
age
sex
occupation
zip_code
0
1
24
M
technician
85711
1
2
53
F
other
94043
2
3
23
M
writer
32067
3
4
24
M
technician
43537
4
5
33
F
other
15213
5
6
42
M
executive
98101
6
7
57
M
administrator
91344
7
8
36
M
administrator
05201
8
9
29
M
student
01002
9
10
53
M
lawyer
90703
对字段进行筛选。
筛选部分字段。
users[['user_id', 'age']].head(5)返回结果如下。
-
user_id
age
0
1
24
1
2
53
2
3
23
3
4
24
4
5
33
排除个别字段,如下所示。
>>> users.exclude('zip_code', 'age').head(5)返回结果如下。
-
user_id
sex
occupation
0
1
M
technician
1
2
F
other
2
3
M
writer
3
4
M
technician
4
5
F
other
排除掉一些字段的同时,通过计算得到一些新的列。例如,将sex为M设置为True,否则设置为False,并将此列取名为sex_bool。如下所示。
>>> users.select(users.exclude('zip_code', 'sex'), sex_bool=users.sex == 'M').head(5)返回结果如下。
-
user_id
age
occupation
sex_bool
0
1
24
technician
True
1
2
53
other
False
2
3
23
writer
True
3
4
24
technician
True
4
5
33
other
False
查询年龄在20~25岁之间的人数,如下所示。
>>> users.age.between(20, 25).count().rename('count') 943查询男女用户的数量。
>>> users.groupby(users.sex).count()返回结果如下。
-
sex
count
0
F
273
1
M
670
将用户按职业划分,从高到底,获取人数最多的前10个职业。
>>> df = users.groupby('occupation').agg(count=users['occupation'].count()) >>> df.sort(df['count'], ascending=False)[:10]返回结果如下。
-
occupation
count
0
student
196
1
other
105
2
educator
95
3
administrator
79
4
engineer
67
5
programmer
66
6
librarian
51
7
writer
45
8
executive
32
9
scientist
31
DataFrame API提供了value_counts方法来快速达到同样的目的。
>>> users.occupation.value_counts()[:10]返回结果如下。
-
occupation
count
0
student
196
1
other
105
2
educator
95
3
administrator
79
4
engineer
67
5
programmer
66
6
librarian
51
7
writer
45
8
executive
32
9
scientist
31
使用更直观的图来查看这份数据。
%matplotlib inline使用横向的柱状图来可视化。
users['occupation'].value_counts().plot(kind='barh', x='occupation', ylabel='prefession')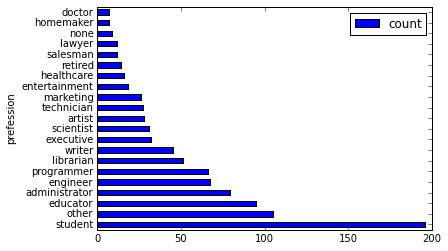
使用直方图来可视化。将年龄分成30组,查看各年龄分布的直方图,如下所示。
>>> users.age.hist(bins=30, title="Distribution of users' ages", xlabel='age', ylabel='count of users')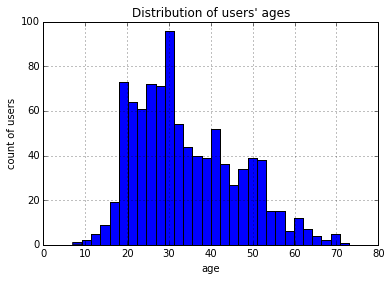
使用JOIN将三张表进行联合后,保存成一张新的表。
movies = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_ml_100k_movies')) ratings = DataFrame(o.get_table('pyodps_ml_100k_ratings')) o.delete_table('pyodps_ml_100k_lens', if_exists=True) lens = movies.join(ratings).join(users).persist('pyodps_ml_100k_lens') lens.dtypes结果如下。
odps.Schema { movie_id int64 title string release_date string video_release_date string imdb_url string user_id int64 rating int64 unix_timestamp int64 age int64 sex string occupation string zip_code string }把0~79岁的年龄,分成8个年龄段。
labels = ['0-9', '10-19', '20-29', '30-39', '40-49', '50-59', '60-69', '70-79'] cut_lens = lens[lens, lens.age.cut(range(0, 80, 10), right=False, labels=labels).rename('年龄分组')]取分组和年龄唯一的前10条数据来进行查看。
>>> cut_lens['年龄分组', 'age'].distinct()[:10]结果如下。
-
年龄分组
age
0
0-9
7
1
10-19
10
2
10-19
11
3
10-19
13
4
10-19
14
5
10-19
15
6
10-19
16
7
10-19
17
8
10-19
18
9
10-19
19
对各个年龄分组下,用户的评分总数和评分均值进行查看,如下所示。
cut_lens.groupby('年龄分组').agg(cut_lens.rating.count().rename('评分总数'), cut_lens.rating.mean().rename('评分均值'))结果如下。
-
年龄分组
评分均值
评分总数
0
0-9
3.767442
43
1
10-19
3.486126
8181
2
20-29
3.467333
39535
3
30-39
3.554444
25696
4
40-49
3.591772
15021
5
50-59
3.635800
8704
6
60-69
3.648875
2623
7
70-79
3.649746
197
