标签传播分类算法是一种用于半监督学习的算法,旨在通过图结构在已标记和未标记的数据点之间传播标签信息。该算法利用数据点之间的相似性构建图,并通过迭代更新节点的标签分布,直到收敛。标签传播算法能够有效地利用少量标记样本的信息,扩展到整个数据集,从而提升分类性能。
算法说明
在算法执行过程中,每个节点的标签按相似度传播给相邻节点,在节点传播的每一步,每个节点根据相邻节点的标签来更新自己的标签。与该节点相似度越大,其相邻节点对其标注的影响权值越大,相似节点的标签越趋于一致,其标签就越容易传播。在标签传播过程中,保持已标注数据的标签不变,使其像一个源头把标签传向未标注数据。最终,当迭代过程结束时,相似节点的概率分布也趋于相似,可以划分到同一个类别中,从而完成标签传播过程。
配置组件
方法一:可视化方式
在Designer工作流页面添加标签传播分类组件,并在界面右侧配置相关参数:
参数类型 | 参数 | 描述 |
字段设置 | 顶点表:选择顶点列 | 点表的点所在列。 |
顶点表:选择标签列 | 点表的点的标签所在列。 | |
顶点表:选择权值列 | 点表的点的权重所在列。 | |
边表:选择源顶点列 | 边表的起点所在列。 | |
边表:选择目标顶点列 | 边表的终点所在列。 | |
边表:选择权值列 | 边表边的权重所在列。 | |
参数设置 | 最大迭代次数 | 最大迭代次数,默认值为30。 |
阻尼系数 | 阻尼系数,默认值为0.8。 | |
收敛系数 | 收敛系数,默认值为0.000001。 | |
执行调优 | 进程数 | 作业并行执行的节点数。数字越大并行度越高,但是框架通讯开销会增大。 |
进程内存 | 单个作业可使用的最大内存量,单位:MB,默认值为4096。 如果实际使用内存超过该值,会抛出 |
方法二:PAI命令方式
使用PAI命令配置标签传播分类组件参数。您可以使用SQL脚本组件进行PAI命令调用,详情请参见场景4:在SQL脚本组件中执行PAI命令。
PAI -name LabelPropagationClassification
-project algo_public
-DinputEdgeTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge
-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id
-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id
-DinputVertexTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node
-DvertexCol=node
-DvertexLabelCol=label
-DoutputTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_result
-DhasEdgeWeight=true
-DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight
-DhasVertexWeight=true
-DvertexWeightCol=label_weight
-Dalpha=0.8
-Depsilon=0.000001;参数 | 是否必选 | 默认值 | 描述 |
inputEdgeTableName | 是 | 无 | 输入边表名。 |
inputEdgeTablePartitions | 否 | 全表读入 | 输入边表的分区。 |
fromVertexCol | 是 | 无 | 输入边表的起点所在列。 |
toVertexCol | 是 | 无 | 输入边表的终点所在列。 |
inputVertexTableName | 是 | 无 | 输入点表名称。 |
inputVertexTablePartitions | 否 | 全表读入 | 输入点表的分区。 |
vertexCol | 是 | 无 | 输入点表的点所在列。 |
outputTableName | 是 | 无 | 输出表名。 |
outputTablePartitions | 否 | 无 | 输出表的分区。 |
lifecycle | 否 | 无 | 输出表的生命周期。 |
workerNum | 否 | 未设置 | 作业并行执行的节点数。数字越大并行度越高,但是框架通讯开销会增大。 |
workerMem | 否 | 4096 | 单个作业可使用的最大内存量,单位:MB,默认值为4096。 如果实际使用内存超过该值,会抛出 |
splitSize | 否 | 64 | 数据切分的大小,单位:MB。 |
hasEdgeWeight | 否 | false | 输入边表的边是否有权重。 |
edgeWeightCol | 否 | 无 | 输入边表边的权重所在列。 |
hasVertexWeight | 否 | false | 输入点表的点是否有权重。 |
vertexWeightCol | 否 | 无 | 输入点表的点的权重所在列。 |
alpha | 否 | 0.8 | 阻尼系数。 |
epsilon | 否 | 0.000001 | 收敛系数。 |
maxIter | 否 | 30 | 最大迭代次数。 |
使用示例
添加SQL脚本组件,去勾选使用Script模式和是否由系统添加Create Table语句,并在SQL脚本中输入以下SQL语句。
drop table if exists LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge; create table LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge as select * from ( select 'a' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id, 0.2 as edge_weight union all select 'a' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id, 0.8 as edge_weight union all select 'b' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id, 1.0 as edge_weight union all select 'd' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id, 1.0 as edge_weight )tmp ; drop table if exists LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node; create table LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node as select * from ( select 'a' as node,'X' as label, 1.0 as label_weight union all select 'd' as node,'Y' as label, 1.0 as label_weight )tmp;对应的数据结构图:
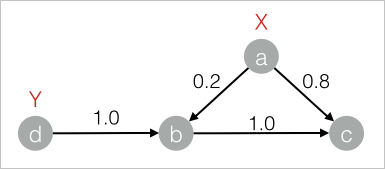
添加SQL脚本组件,去勾选使用Script模式和是否由系统添加Create Table语句,在SQL脚本中输入以下PAI命令,并将步骤 1和步骤 2的组件进行连线。
drop table if exists ${o1}; PAI -name LabelPropagationClassification -project algo_public -DinputEdgeTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge -DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id -DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id -DinputVertexTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node -DvertexCol=node -DvertexLabelCol=label -DoutputTableName=${o1} -DhasEdgeWeight=true -DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight -DhasVertexWeight=true -DvertexWeightCol=label_weight -Dalpha=0.8 -Depsilon=0.000001;单击左上角
 ,运行工作流。
,运行工作流。待运行结束,右键单击步骤 2的组件,选择查看数据 > SQL脚本的输出,查看训练结果。
| node | tag | weight | | ---- | --- | ------------------- | | a | X | 1.0 | | c | X | 0.5370370370370371 | | c | Y | 0.4629629629629629 | | b | X | 0.16666666666666666 | | b | Y | 0.8333333333333333 | | d | Y | 1.0 |
